AcoC
- Description: acetoin dehydrogenase E2 component (dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase)
| Gene name | acoC |
| Synonyms | yfjI |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetoin dehydrogenase E2 component (dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase) |
| Function | acetoin utilization |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: AcoC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 6.524 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1194 bp, 398 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | acoB, acoL |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 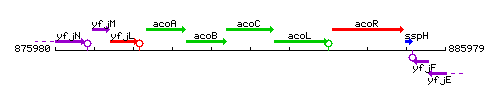
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources
This gene is a member of the following regulons
AcoR regulon, CcpA regulon, SigL regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU08080
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acetyl-CoA + enzyme N(6)-(dihydrolipoyl)lysine = CoA + enzyme N(6)-(S-acetyldihydrolipoyl)lysine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: lipoyl-binding domain (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: Membrane-proximal (Spotty) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O31550
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.3.1.12
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Michel Debarbouille, Pasteur Institute, Paris, France Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Lehnik-Habrink M, Schaffer M, Mäder U, Diethmaier C, Herzberg C, Stülke J RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol Microbiol. 2011 81(6): 1459-1473. PubMed:21815947
Jean-Christophe Meile, Ling Juan Wu, S Dusko Ehrlich, Jeff Errington, Philippe Noirot
Systematic localisation of proteins fused to the green fluorescent protein in Bacillus subtilis: identification of new proteins at the DNA replication factory.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2135-46
[PubMed:16479537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Heike Reents, Richard Münch, Thorben Dammeyer, Dieter Jahn, Elisabeth Härtig
The Fnr regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(3);1103-12
[PubMed:16428414]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Hambraeus, C von Wachenfeldt, L Hederstedt
Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2003, 269(5);706-14
[PubMed:12884008]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N O Ali, J Bignon, G Rapoport, M Debarbouille
Regulation of the acetoin catabolic pathway is controlled by sigma L in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(8);2497-504
[PubMed:11274109]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Miwa, A Nakata, A Ogiwara, M Yamamoto, Y Fujita
Evaluation and characterization of catabolite-responsive elements (cre) of Bacillus subtilis.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2000, 28(5);1206-10
[PubMed:10666464]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
M Huang, F B Oppermann-Sanio, A Steinbüchel
Biochemical and molecular characterization of the Bacillus subtilis acetoin catabolic pathway.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(12);3837-41
[PubMed:10368162]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)