YesT
- Description: rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase
| Gene name | yesT |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | rhamnogalacturonan esterase |
| Function | pectin utilization |
| MW, pI | 25 kDa, 5.505 |
| Gene length, protein length | 696 bp, 232 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yesS, yesU |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 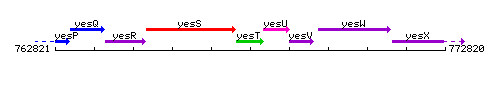
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU07020
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: 'GDSL' lipolytic enzyme family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O31523
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Sandrine Poncet, Maryline Soret, Peggy Mervelet, Josef Deutscher, Philippe Noirot
Transcriptional activator YesS is stimulated by histidine-phosphorylated HPr of the Bacillus subtilis phosphotransferase system.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(41);28188-28197
[PubMed:19651770]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Irene Martínez-Martínez, José Navarro-Fernández, José Daniel Lozada-Ramírez, Francisco García-Carmona, Alvaro Sánchez-Ferrer
YesT: a new rhamnogalacturonan acetyl esterase from Bacillus subtilis.
Proteins: 2008, 71(1);379-88
[PubMed:17957779]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Akihito Ochiai, Takafumi Itoh, Akiko Kawamata, Wataru Hashimoto, Kousaku Murata
Plant cell wall degradation by saprophytic Bacillus subtilis strains: gene clusters responsible for rhamnogalacturonan depolymerization.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2007, 73(12);3803-13
[PubMed:17449691]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)