McpC
- Description: membrane-bound chemotaxis receptor for proline, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein
| Gene name | mcpC |
| Synonyms | prg71 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein |
| Function | control of chemotaxis threonine, glycine, serine, lysine, valine and arginine |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mcpC | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: McpC | |
| MW, pI | 71 kDa, 5.174 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1962 bp, 654 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ykwB, ykwC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 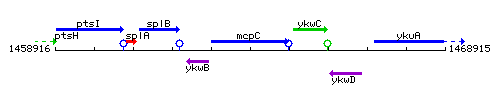
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed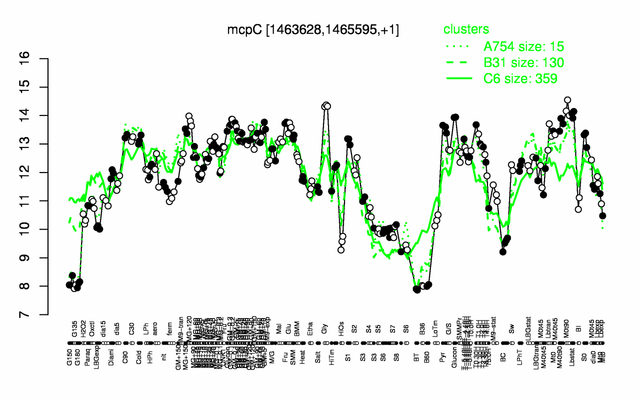
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
motility and chemotaxis, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13950
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13950
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13950
- Structure:
- UniProt: P54576
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
George D Glekas, Brendan J Mulhern, Abigail Kroc, Keegan A Duelfer, Victor Lei, Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
The Bacillus subtilis chemoreceptor McpC senses multiple ligands using two discrete mechanisms.
J Biol Chem: 2012, 287(47);39412-8
[PubMed:23038252]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Vincent J Cannistraro, George D Glekas, Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
Cellular stoichiometry of the chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(13);3220-7
[PubMed:21515776]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hendrik Szurmant, Michael W Bunn, Stephen H Cho, George W Ordal
Ligand-induced conformational changes in the Bacillus subtilis chemoreceptor McpB determined by disulfide crosslinking in vivo.
J Mol Biol: 2004, 344(4);919-28
[PubMed:15544802]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christopher J Kristich, George W Ordal
Analysis of chimeric chemoreceptors in Bacillus subtilis reveals a role for CheD in the function of the McpC HAMP domain.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(17);5950-5
[PubMed:15317802]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Christopher J Kristich, George D Glekas, George W Ordal
The conserved cytoplasmic module of the transmembrane chemoreceptor McpC mediates carbohydrate chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 47(5);1353-66
[PubMed:12603740]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L F Garrity, S L Schiel, R Merrill, J Reizer, M H Saier, G W Ordal
Unique regulation of carbohydrate chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis by the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system and the methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein McpC.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(17);4475-80
[PubMed:9721285]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jakob Müller, Stacey Schiel, George W Ordal, Hans H Saxild
Functional and genetic characterization of mcpC, which encodes a third methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 10);3231-3240
[PubMed:9353924]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D W Hanlon, C Ying, G W Ordal
Purification and reconstitution of the methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 1993, 1158(3);345-51
[PubMed:8251536]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M S Thoelke, J M Casper, G W Ordal
Methyl group turnover on methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins during chemotaxis by Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 1990, 265(4);1928-32
[PubMed:2105313]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
M S Thoelke, J R Kirby, G W Ordal
Novel methyl transfer during chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis.
Biochemistry: 1989, 28(13);5585-9
[PubMed:2505839]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J A Ahlgren, G W Ordal
Methyl esterification of glutamic acid residues of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Biochem J: 1983, 213(3);759-63
[PubMed:6137212]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)