PhoP
- Description: two-component response regulator, regulation of phosphate metabolism
| Gene name | phoP |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component response regulator |
| Function | regulation of phosphate metabolism (phoA, phoB, phoD, resABCDE, tagA-tagB, tagDEF, tuaA-H) |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: phoP | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PhoP | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: phoP | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 5.068 |
| Gene length, protein length | 720 bp, 240 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | phoR, mdh |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 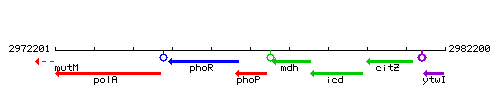
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
phosphate metabolism, transcription factors and their control, regulators of core metabolism, sporulation proteins, general stress proteins (controlled by SigB), membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CcpA regulon, PhoP regulon, SigB regulon, SigE regulon
The PhoP regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29110
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation by PhoR under conditions of phosphate limitation (stimulates DNA-binding activity)
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: phosphorylation stimulates DNA-binding activity
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure: 1MVO (receiver domain)
- UniProt: P13792
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Marion Hulett, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Regulation of phoP-phoR expression
Bindiya Kaushal, Salbi Paul, F Marion Hulett
Direct regulation of Bacillus subtilis phoPR transcription by transition state regulator ScoC.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(12);3103-13
[PubMed:20382764]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ankita Puri-Taneja, Salbi Paul, Yinghua Chen, F Marion Hulett
CcpA causes repression of the phoPR promoter through a novel transcription start site, P(A6).
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(4);1266-78
[PubMed:16452408]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Salbi Paul, Stephanie Birkey, Wei Liu, F Marion Hulett
Autoinduction of Bacillus subtilis phoPR operon transcription results from enhanced transcription from EsigmaA- and EsigmaE-responsive promoters by phosphorylated PhoP.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(13);4262-75
[PubMed:15205429]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Zoltán Prágai, Nicholas E E Allenby, Nicola O'Connor, Sarah Dubrac, Georges Rapoport, Tarek Msadek, Colin R Harwood
Transcriptional regulation of the phoPR operon in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(4);1182-90
[PubMed:14762014]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Biochemical analyses
Targets of PhoR
Additional publications: PubMed
Other original publications
Matthew Schau, Amr Eldakak, F Marion Hulett
Terminal oxidases are essential to bypass the requirement for ResD for full Pho induction in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(24);8424-32
[PubMed:15576792]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)