YfkC
- Description: mechanosensitive channel, similar to MscS
| Gene name | yfkC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | mechanosensitive channel, similar to MscS |
| Function | resistance to osmotic downshock |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yfkC | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.293 |
| Gene length, protein length | 840 bp, 280 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yfkD, yfkA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 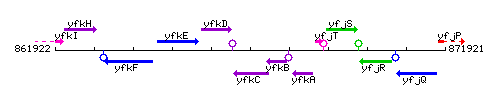
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed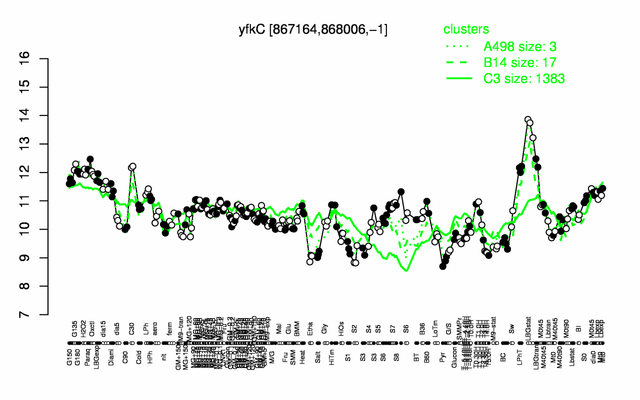
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
coping with hypo-osmotic stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU07940
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O35043
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Erhard Bremer, University of Marburg, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Pierre Nicolas, Ulrike Mäder, Etienne Dervyn, Tatiana Rochat, Aurélie Leduc, Nathalie Pigeonneau, Elena Bidnenko, Elodie Marchadier, Mark Hoebeke, Stéphane Aymerich, Dörte Becher, Paola Bisicchia, Eric Botella, Olivier Delumeau, Geoff Doherty, Emma L Denham, Mark J Fogg, Vincent Fromion, Anne Goelzer, Annette Hansen, Elisabeth Härtig, Colin R Harwood, Georg Homuth, Hanne Jarmer, Matthieu Jules, Edda Klipp, Ludovic Le Chat, François Lecointe, Peter Lewis, Wolfram Liebermeister, Anika March, Ruben A T Mars, Priyanka Nannapaneni, David Noone, Susanne Pohl, Bernd Rinn, Frank Rügheimer, Praveen K Sappa, Franck Samson, Marc Schaffer, Benno Schwikowski, Leif Steil, Jörg Stülke, Thomas Wiegert, Kevin M Devine, Anthony J Wilkinson, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Michael Hecker, Uwe Völker, Philippe Bessières, Philippe Noirot
Condition-dependent transcriptome reveals high-level regulatory architecture in Bacillus subtilis.
Science: 2012, 335(6072);1103-6
[PubMed:22383849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paul G Wahome, Ann E Cowan, Barbara Setlow, Peter Setlow
Levels and localization of mechanosensitive channel proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Arch Microbiol: 2009, 191(5);403-14
[PubMed:19252899]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tamara Hoffmann, Clara Boiangiu, Susanne Moses, Erhard Bremer
Responses of Bacillus subtilis to hypotonic challenges: physiological contributions of mechanosensitive channels to cellular survival.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2008, 74(8);2454-60
[PubMed:18310427]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paul G Wahome, Peter Setlow
Growth, osmotic downshock resistance and differentiation of Bacillus subtilis strains lacking mechanosensitive channels.
Arch Microbiol: 2008, 189(1);49-58
[PubMed:17665170]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)