NagB
- Description: glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase
| Gene name | nagB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase |
| Function | N-acetylglucosamine utilization |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: nagB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism, Murein recycling | |
| MW, pI | 26 kDa, 5.717 |
| Gene length, protein length | 726 bp, 242 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | nagA, nagR |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 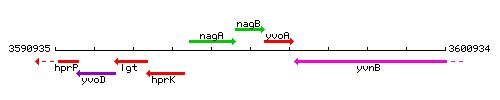
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed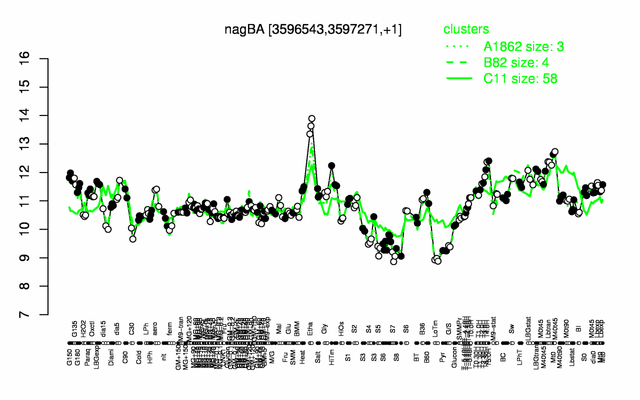
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall degradation/ turnover, utilization of specific carbon sources
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35020
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
- A mutation was found in this gene after evolution under relaxed selection for sporulation PubMed
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: D-glucosamine 6-phosphate + H2O = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NH3 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: NagB subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): GamA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: O35000
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Christopher T Brown, Laura K Fishwick, Binna M Chokshi, Marissa A Cuff, Jay M Jackson, Travis Oglesby, Alison T Rioux, Enrique Rodriguez, Gregory S Stupp, Austin H Trupp, James S Woollcombe-Clarke, Tracy N Wright, William J Zaragoza, Jennifer C Drew, Eric W Triplett, Wayne L Nicholson
Whole-genome sequencing and phenotypic analysis of Bacillus subtilis mutants following evolution under conditions of relaxed selection for sporulation.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2011, 77(19);6867-77
[PubMed:21821766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Florence Vincent, Gideon J Davies, James A Brannigan
Structure and kinetics of a monomeric glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase: missing link of the NagB superfamily?
J Biol Chem: 2005, 280(20);19649-55
[PubMed:15755726]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H L Mobley, R J Doyle, U N Streips, S O Langemeier
Transport and incorporation of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1982, 150(1);8-15
[PubMed:6174502]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)