YqgQ
Revision as of 08:29, 20 April 2012 by 134.76.70.252 (talk)
- Description: putative single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein
| Gene name | yqgQ |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | unknown |
| MW, pI | 8 kDa, 5.137 |
| Gene length, protein length | 213 bp, 71 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | glcK, yqgP |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 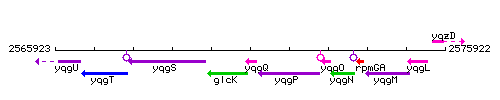
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
poorly characterized/ putative enzymes
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU24860
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- UniProt: P54494
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Damodharan Lakshminarasimhan, Subramaniam Eswaramoorthy, Stephen K Burley, Subramanyam Swaminathan
Structure of YqgQ protein from Bacillus subtilis, a conserved hypothetical protein.
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun: 2010, 66(Pt 1);8-11
[PubMed:20057058]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Lili R Mesak, Felix M Mesak, Michael K Dahl
Expression of a novel gene, gluP, is essential for normal Bacillus subtilis cell division and contributes to glucose export.
BMC Microbiol: 2004, 4;13
[PubMed:15050034]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)