MscL
- Description: large conductance mechanosensitive channel protein, prevents selective release of cytoplasmic proteins in a hypotonic environment
| Gene name | mscL |
| Synonyms | ywpC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | large conductance mechanosensitive channel protein |
| Function | resistance to osmotic downshockglycine betaine export |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 4.649 |
| Gene length, protein length | 390 bp, 130 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywpD, ywpB |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 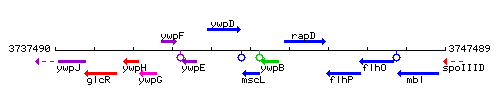
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
coping with hypo-osmotic stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36360
Phenotypes of a mutant
sensitive to osmotic downshock (> 0.5 M) during logarithmic growth PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: mscL family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P94585
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: mscL PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: expressed in logarithmic phase PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jan Maarten van Dijl, Groningen, Netherlands
Erhard Bremer, University of Marburg, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Thijs R H M Kouwen, Erik N Trip, Emma L Denham, Mark J J B Sibbald, Jean-Yves F Dubois, Jan Maarten van Dijl
The large mechanosensitive channel MscL determines bacterial susceptibility to the bacteriocin sublancin 168.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother: 2009, 53(11);4702-11
[PubMed:19738010]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Zhenfeng Liu, Chris S Gandhi, Douglas C Rees
Structure of a tetrameric MscL in an expanded intermediate state.
Nature: 2009, 461(7260);120-4
[PubMed:19701184]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paul G Wahome, Ann E Cowan, Barbara Setlow, Peter Setlow
Levels and localization of mechanosensitive channel proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
Arch Microbiol: 2009, 191(5);403-14
[PubMed:19252899]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Thijs R H M Kouwen, Haike Antelmann, René van der Ploeg, Emma L Denham, Michael Hecker, Jan Maarten van Dijl
MscL of Bacillus subtilis prevents selective release of cytoplasmic proteins in a hypotonic environment.
Proteomics: 2009, 9(4);1033-43
[PubMed:19160392]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Tamara Hoffmann, Clara Boiangiu, Susanne Moses, Erhard Bremer
Responses of Bacillus subtilis to hypotonic challenges: physiological contributions of mechanosensitive channels to cellular survival.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2008, 74(8);2454-60
[PubMed:18310427]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Paul G Wahome, Peter Setlow
Growth, osmotic downshock resistance and differentiation of Bacillus subtilis strains lacking mechanosensitive channels.
Arch Microbiol: 2008, 189(1);49-58
[PubMed:17665170]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Paul G Wahome, Peter Setlow
The synthesis and role of the mechanosensitive channel of large conductance in growth and differentiation of Bacillus subtilis.
Arch Microbiol: 2006, 186(5);377-83
[PubMed:16897034]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P C Moe, P Blount, C Kung
Functional and structural conservation in the mechanosensitive channel MscL implicates elements crucial for mechanosensation.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 28(3);583-92
[PubMed:9632260]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Presecan, I Moszer, L Boursier, H Cruz Ramos, V de la Fuente, M-F Hullo, C Lelong, S Schleich, A Sekowska, B H Song, G Villani, F Kunst, A Danchin, P Glaser
The Bacillus subtilis genome from gerBC (311 degrees) to licR (334 degrees).
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 10);3313-3328
[PubMed:9353933]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)