Easter egg
- Description: RNA component of RNase P
| Gene name | rnpB |
| Synonyms | rnaP |
| Essential | no |
| Product | RNA component of ribonuclease P (RNase P) (catalytic subunit, ribozyme) |
| Function | cleavage of precursor sequences from the 5' ends of pre-tRNAs |
| Gene length | 401 bp |
| Immediate neighbours | ypsC, ypsB |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | |
Genetic context 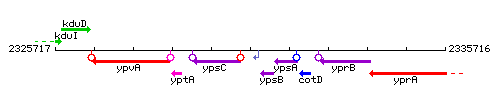
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
The RNA
- Biological activity: 5' end maturation of precursor tRNAs
- RNA family:
- cofactor: divalent cations (Ca(II) or Mg (II)) for the stabilization of the complex with pre-tRNA PubMed
- interaction: RnpA-RnpB
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/RNA
- Carol Fierke, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, USA homepage
- Roland Hartmann, Marburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications