PyrB
- Description: aspartate carbamoyltransferase
| Gene name | pyrB |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | aspartate carbamoyltransferase |
| Function | pyrimidine biosynthesis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Pyrimidines, Nucleotides (regulation) | |
| MW, pI | 34 kDa, 5.341 |
| Gene length, protein length | 912 bp, 304 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | pyrP, pyrC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 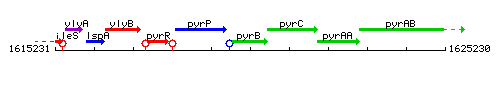
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15490
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of nucleotides, phosphoproteins
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Carbamoyl phosphate + L-aspartate = phosphate + N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: ATCase/OTCase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-303 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure: 2AT2
- UniProt: P05654
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.1.3.2
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulatory mechanism:
- PyrR: RNA switch, transcription termination/ antitermination (in the presence of uridine nucleotides: termination, in their absence: antitermination) PubMed
- Additional information: subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Birgit Hobl, Matthias Mack
The regulator protein PyrR of Bacillus subtilis specifically interacts in vivo with three untranslated regions within pyr mRNA of pyrimidine biosynthesis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2007, 153(Pt 3);693-700
[PubMed:17322189]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris Macek, Ivan Mijakovic, Jesper V Olsen, Florian Gnad, Chanchal Kumar, Peter R Jensen, Matthias Mann
The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Cell Proteomics: 2007, 6(4);697-707
[PubMed:17218307]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hesheng Zhang, Robert L Switzer
Transcriptional pausing in the Bacillus subtilis pyr operon in vitro: a role in transcriptional attenuation?
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(16);4764-71
[PubMed:12896995]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Lu, R J Turner, R L Switzer
Roles of the three transcriptional attenuators of the Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine biosynthetic operon in the regulation of its expression.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(5);1315-25
[PubMed:7868607]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
P Hu, R L Switzer
Evidence for substrate stabilization in regulation of the degradation of Bacillus subtilis aspartate transcarbamylase in vivo.
Arch Biochem Biophys: 1995, 316(1);260-6
[PubMed:7840626]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R J Turner, Y Lu, R L Switzer
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine biosynthetic (pyr) gene cluster by an autogenous transcriptional attenuation mechanism.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(12);3708-22
[PubMed:8206849]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C L Quinn, B T Stephenson, R L Switzer
Functional organization and nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus subtilis pyrimidine biosynthetic operon.
J Biol Chem: 1991, 266(14);9113-27
[PubMed:1709162]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
C G Lerner, R L Switzer
Cloning and structure of the Bacillus subtilis aspartate transcarbamylase gene (pyrB).
J Biol Chem: 1986, 261(24);11156-65
[PubMed:3015959]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
J S Brabson, M R Maurizi, R L Switzer
Aspartate transcarbamylase from Bacillus subtilis.
Methods Enzymol: 1985, 113;627-35
[PubMed:3937019]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
R W Bond, R L Switzer
Degradation of aspartate transcarbamylase in Bacillus subtilis is deficient in rel mutants but is not mediated by guanosine polyphosphates.
J Bacteriol: 1984, 158(2);746-8
[PubMed:6427186]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)