DegU
- Description: two-component response regulator, regulation of degradative enzyme and genetic competence, involved in activation of capsule biosynthetic operon expression (together with SwrAA), non-phosphorylated DegU is required for swarming motility PubMed
| Gene name | degU |
| Synonyms | sacU, iep |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component response regulator |
| Function | regulation of degradative enzyme and genetic competence
of genetic competence |
| MW, pI | 25 kDa, 5.602 |
| Gene length, protein length | 687 bp, 229 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yviA, degS |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 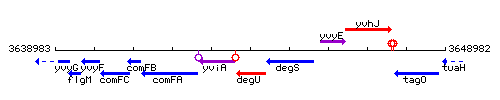
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU35490
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcription activator of degradative enzyme genes (sacB and degQ) and of comK expression
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes controlled by DegU
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Cofactor(s):
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P13800
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications