Difference between revisions of "LicT"
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
'''LicT-RNA interaction''' | '''LicT-RNA interaction''' | ||
<pubmed>11953318,1279678, 10610766,18682383</pubmed> | <pubmed>11953318,1279678, 10610766,18682383</pubmed> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 17:28, 15 June 2009
- Description: transcriptional antiterminator of the bglPH operon
| Gene name | licT |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator (BglG family) |
| Function | required for substrate-dependent induction of bglPH |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 5.944 |
| Gene length, protein length | 831 bp, 277 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | bglS, yxiP |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 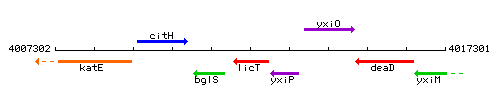
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU39080
Phenotypes of a mutant
no expression of the bglP-bglH operon
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binding to the mRNAs of bglS and the bglP-bglH operon, causes transcription antitermination (in presence of salicin and absence of glucose)
- Protein family: transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: P39805
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Stephane Aymerich, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Josef Deutscher, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Michael Hecker, Greifswald, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Original description
Control of LicT activity
Structural analysis of LicT
LicT-RNA interaction
Hélène Déméné, Thierry Ducat, Karine De Guillen, Catherine Birck, Stéphane Aymerich, Michel Kochoyan, Nathalie Declerck
Structural mechanism of signal transduction between the RNA-binding domain and the phosphotransferase system regulation domain of the LicT antiterminator.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(45);30838-49
[PubMed:18682383]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Yinshan Yang, Nathalie Declerck, Xavier Manival, Stéphane Aymerich, Michel Kochoyan
Solution structure of the LicT-RNA antitermination complex: CAT clamping RAT.
EMBO J: 2002, 21(8);1987-97
[PubMed:11953318]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Declerck, F Vincent, F Hoh, S Aymerich, H van Tilbeurgh
RNA recognition by transcriptional antiterminators of the BglG/SacY family: functional and structural comparison of the CAT domain from SacY and LicT.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 294(2);389-402
[PubMed:10610766]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Aymerich, M Steinmetz
Specificity determinants and structural features in the RNA target of the bacterial antiterminator proteins of the BglG/SacY family.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1992, 89(21);10410-4
[PubMed:1279678]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)