Difference between revisions of "SepF"
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| + | ** repressed under conditions that trigger sporulation ([[Spo0A]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/14651647 PubMed] | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| + | ** [[Spo0A]]: transcription repression [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/14651647 PubMed] | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 11 June 2009
- Description: part of the divisome
| Gene name | sepF |
| Synonyms | ylmF |
| Essential | no |
| Product | FtsZ-interacting protein |
| Function | proper execution of septum synthesis |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 4.863 |
| Gene length, protein length | 447 bp, 149 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ylmE, ylmG |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 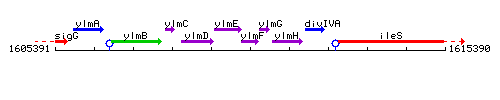
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU15390
Phenotypes of a mutant
Less efficient cell division results in longer cells. Electron microscopy reveals strongly distorted division septa.
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
Cell division
- Protein family: sepF family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot), Septum
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: O31728
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Leendert Hamoen, CBCB, Newcastle University, UK
Your additional remarks
SepF mutation is synthetic lethal in combination with an ezrA mutation or an ftsA mutation.
References
- Hamoen et al. (2006) SepF, a novel FtsZ-interacting protein required for a late step in cell division Mol. Microbiol. 59(3): 989-99. Pubmed
- Ishikawa et al. (2006) A new FtsZ-interacting protein, YlmF, complements the activity of FtsA during progression of cell division in Bacillus subtilis Mol. Microbiol. 60(6): 1364-80. Pubmed