Difference between revisions of "Sandbox"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' | + | * '''Description:''' acetate kinase <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Gene name''' | ||
| − | |'' | + | |''ackA'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || '' | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Synonyms''' || '' '' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || acetate kinase |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || overflow metabolism |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 42 kDa, 5.191 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Gene length, protein length''' || 1185 bp, 395 aa |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[ | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[moaB]]'', ''[[ytxK]]'' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS: | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Get the DNA and protein [http://srs.ebi.ac.uk/srsbin/cgi-bin/wgetz?-e+[EMBLCDS:CAB14925]+-newId sequences] <br/> (Barbe ''et al.'', 2009)''' |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image: | + | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:ackA_context.gif]] |
<div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | <div align="right"> <small>This image was kindly provided by [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/ SubtiList]</small></div> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * '''Locus tag:''' | + | * '''Locus tag:''' BSU29470 |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ | + | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/ackA.html] |
| − | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+ | + | * '''SubtiList entry:''' [http://genolist.pasteur.fr/SubtiList/genome.cgi?gene_detail+BG10813] |
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 52: | ||
=== Basic information/ Evolution === | === Basic information/ Evolution === | ||
| − | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' | + | * '''Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:''' ATP + acetate = ADP + acetyl phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot) |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * '''Protein family:''' acetokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot) | |
| − | * ''' | + | * '''Paralogous protein(s):''' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| Line 76: | Line 68: | ||
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
| − | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | + | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' |
| − | * '''Interactions:''' | + | * '''Interactions:''' |
| − | * '''Localization:''' | + | * '''Localization:''' cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot) |
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' |
| − | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/ | + | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P37877 P37877] |
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+ | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu+BSU29470] |
| + | |||
| + | * '''E.C. number:''' [http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/2.7.2.1 2.7.2.1] | ||
=== Additional information=== | === Additional information=== | ||
| − | |||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' | + | * '''Operon:''' |
| − | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
| − | * '''Regulation:''' | + | * '''Regulation:''' expression activated by glucose (2.5 fold) (CcpA) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12850135 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | + | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' |
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 107: | Line 100: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' | + | * '''Mutant:''' |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
| Line 121: | Line 114: | ||
=Labs working on this gene/protein= | =Labs working on this gene/protein= | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Linc Sonenshein|Linc Sonenshein]], Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA [http://www.tufts.edu/sackler/microbiology/faculty/sonenshein/index.html Homepage] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Your additional remarks= | =Your additional remarks= | ||
| Line 129: | Line 120: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12850135 8226682 9811655, </pubmed> |
| − | # | + | # Blencke et al. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in ''Bacillus subtilis'': regulation of the central metabolic pathways. ''Metab Eng.'' '''5:''' 133-149 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12850135 PubMed] |
| − | + | # Grundy FJ, Waters DA, Allen SH, Henkin TM (1993) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA. J Bacteriol 175:7348-7355 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8226682 PubMed] | |
| − | # | + | # Turinsky, A. J., Grundy, F. J., Kim, J. H., Chambliss, G. H., and Henkin, T. M. 1998. Transcriptional activation of the Bacillus subtilis ackA gene requires sequences upstream of the promoter. J. Bacteriol. 180: 5961-5967. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/9811655 PubMed] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | # | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | # Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 8 June 2009
- Description: acetate kinase
| Gene name | ackA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetate kinase |
| Function | overflow metabolism |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 5.191 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1185 bp, 395 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | moaB, ytxK |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 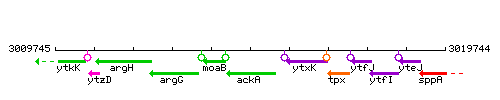
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29470
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + acetate = ADP + acetyl phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: acetokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P37877
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation: expression activated by glucose (2.5 fold) (CcpA) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Blencke et al. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways. Metab Eng. 5: 133-149 PubMed
- Grundy FJ, Waters DA, Allen SH, Henkin TM (1993) Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis acetate kinase gene by CcpA. J Bacteriol 175:7348-7355 PubMed
- Turinsky, A. J., Grundy, F. J., Kim, J. H., Chambliss, G. H., and Henkin, T. M. 1998. Transcriptional activation of the Bacillus subtilis ackA gene requires sequences upstream of the promoter. J. Bacteriol. 180: 5961-5967. PubMed
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed