Difference between revisions of "YxkO"
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
* '''Sigma factor:''' ''[[SigB]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15805528 PubMed] | * '''Sigma factor:''' ''[[SigB]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15805528 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''Regulation:''' | + | * '''Regulation:''' induced by stress ([[SigB]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15805528 PubMed] |
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
Revision as of 08:07, 30 March 2009
- Description: general stress protein, survival of ethanol stress
| Gene name | yxkO |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | unknown |
| Function | survival of ethanol stress |
| MW, pI | 29 kDa, 5.488 |
| Gene length, protein length | 828 bp, 276 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yxlA, cydD |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 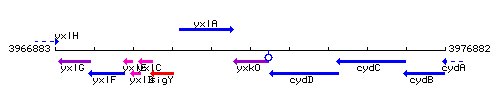
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody: