Difference between revisions of "LeuA"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * '''Description:''' | + | * '''Description:''' 2-isopropylmalate synthase <br/><br/> |
{| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | {| align="right" border="1" cellpadding="2" | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Essential''' || no | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || 2-isopropylmalate synthase | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''Product''' || 2-isopropylmalate synthase |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || leucine | + | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || biosynthesis of leucine |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 56 kDa, 5.657 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 56 kDa, 5.657 | ||
Revision as of 16:44, 16 March 2009
- Description: 2-isopropylmalate synthase
| Gene name | leuA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | 2-isopropylmalate synthase |
| Function | biosynthesis of leucine |
| MW, pI | 56 kDa, 5.657 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1554 bp, 518 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | leuB, ilvC |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 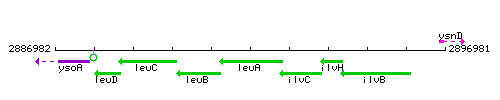
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates:
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry:
- KEGG entry:
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulation: expressed in the absence of branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), expression is stimulated in the presence of glucose PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: glucose regulation: CcpA PubMed, repression by BCAA: tRNA-controlled RNA switch (T-box) that mediates termination/antitermination, transcription repression by CodY
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed