Difference between revisions of "RecF"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
<pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 22933559 </pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed>2987848, 15186413 9207023 24285298 24891441</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>2987848, 15186413 9207023 24285298 24891441 8510642</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 11:16, 10 August 2015
- Description: promoter of RecA DNA repair center assembly
| Gene name | recF |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | |
| Product | promoter of RecA DNA repair center assembly |
| Function | DNA repair/ recombination |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: RecF | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 7.015 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1110 bp, 370 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yaaA, yaaB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 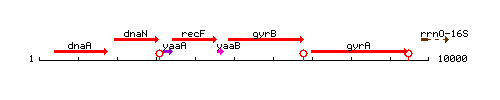
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed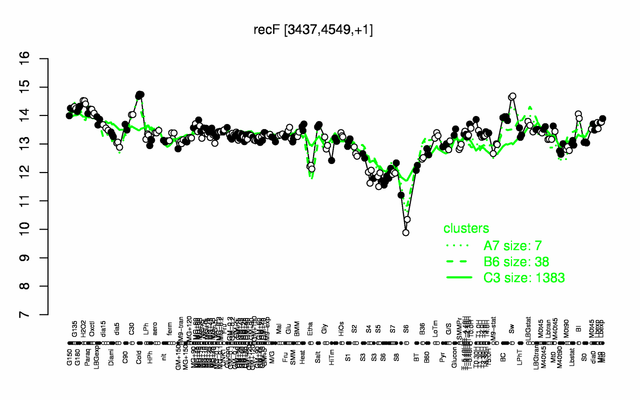
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00040
Phenotypes of a mutant
- drastically reduced survival of mature dormant spores after exposure to ultrahigh vacuum desiccation and ionizing radiation that induce single strand (ss) DNA nicks and double-strand breaks (DSBs) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00040
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: recF family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU00040
- Structure:
- UniProt: P05651
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Justin S Lenhart, Jeremy W Schroeder, Brian W Walsh, Lyle A Simmons
DNA repair and genome maintenance in Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);530-64
[PubMed:22933559]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Justin S Lenhart, Eileen R Brandes, Jeremy W Schroeder, Roderick J Sorenson, Hollis D Showalter, Lyle A Simmons
RecO and RecR are necessary for RecA loading in response to DNA damage and replication fork stress.
J Bacteriol: 2014, 196(15);2851-60
[PubMed:24891441]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ignacija Vlašić, Ramona Mertens, Elena M Seco, Begoña Carrasco, Silvia Ayora, Günther Reitz, Fabian M Commichau, Juan C Alonso, Ralf Moeller
Bacillus subtilis RecA and its accessory factors, RecF, RecO, RecR and RecX, are required for spore resistance to DNA double-strand break.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2014, 42(4);2295-307
[PubMed:24285298]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Dawit Kidane, Humberto Sanchez, Juan C Alonso, Peter L Graumann
Visualization of DNA double-strand break repair in live bacteria reveals dynamic recruitment of Bacillus subtilis RecF, RecO and RecN proteins to distinct sites on the nucleoids.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 52(6);1627-39
[PubMed:15186413]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Ayora, J C Alonso
Purification and characterization of the RecF protein from Bacillus subtilis 168.
Nucleic Acids Res: 1997, 25(14);2766-72
[PubMed:9207023]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J C Alonso, A C Stiege, G Lüder
Genetic recombination in Bacillus subtilis 168: effect of recN, recF, recH and addAB mutations on DNA repair and recombination.
Mol Gen Genet: 1993, 239(1-2);129-36
[PubMed:8510642]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
N Ogasawara, S Moriya, H Yoshikawa
Structure and function of the region of the replication origin of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. IV. Transcription of the oriC region and expression of DNA gyrase genes and other open reading frames.
Nucleic Acids Res: 1985, 13(7);2267-79
[PubMed:2987848]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)