Difference between revisions of "CheV"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
| − | ** DS70 (mls in NCIB3610) {{PubMed|12864845}} | + | ** DS70 (''cheV''::''mls'' in NCIB3610) {{PubMed|12864845}} |
| − | ** TB183 ''amyE''::Phy-''sfgfp'' (mls in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed ''sfgfp'') {{PubMed|26122431}} | + | ** TB183 ''amyE''::Phy-''sfgfp'' (''cheV''::''mls'' in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed ''sfgfp'') {{PubMed|26122431}} |
| − | ** TB199 ''amyE''::Phy-''mKATE2'' (mls in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed ''mKATE2'') {{PubMed|26122431}} | + | ** TB199 ''amyE''::Phy-''mKATE2'' (''cheV''::''mls'' in NCIB3610 with constitutive expressed ''mKATE2'') {{PubMed|26122431}} |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
Revision as of 06:18, 3 July 2015
- Description: modulation of CheA activity in response to attractants
| Gene name | cheV |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | CheA modulator |
| Function | control of CheA activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cheV | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: CheV | |
| MW, pI | 34 kDa, 4.617 |
| Gene length, protein length | 909 bp, 303 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ykzT, kre |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed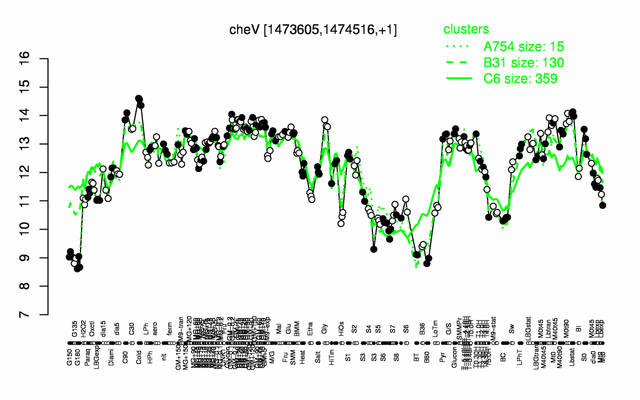
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transcription factors and their control, phosphoproteins, motility and chemotaxis
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU14010
Phenotypes of a mutant
- cheV cheW double mutants exhibit complete loss of chemotaxis PubMed
- not essential for pellicle biofilm formation, but mutant is outcompeted by the wild-type strain when competed during pellicle formation PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14010
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): CheW (N-terminal domain of CheV)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification: the C-terminal two-component receiver domain is phosphorylated on a Asp residue by CheA PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- forms lateral clusters (phosphorylated form), but in the presence of high asparagine concentration (non-phosphorylated form) there is a reversible re-localization to the poles of the cell PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU14010
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37599
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Christopher V Rao, George D Glekas, George W Ordal
The three adaptation systems of Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
Trends Microbiol: 2008, 16(10);480-7
[PubMed:18774298]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications