Difference between revisions of "PgpH"
| Line 135: | Line 135: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | ==Reviews== | ||
| + | <pubmed>25637595</pubmed> | ||
| + | ==Original publications== | ||
<pubmed>21630458 25583510 </pubmed> | <pubmed>21630458 25583510 </pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 15:49, 1 February 2015
- Description: c-di-AMP specific phosphodiesterase
| Gene name | yqfF |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | c-di-AMP specific phosphodiesterase |
| Function | control of c-di-AMP homeostasis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yqfF | |
| MW, pI | 78 kDa, 7.697 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2133 bp, 711 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yqfG, phoH |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 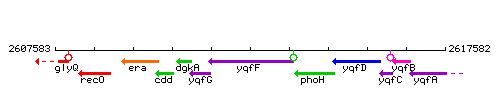
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
metabolism of signalling nucleotides
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU25330
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU25330
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- hydrolysis of c-di-AMP to 5'-pApA PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- YqfF is a member of a suspected group of hubs proteins that were suggested to be involved in a large number of interactions PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU25330
- Structure:
- UniProt: P46344
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- SM-GN1 (yqfF-spc), available in Anne Galinier's and Boris Görke's labs
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
TuAnh Ngoc Huynh, Shukun Luo, Daniel Pensinger, John-Demian Sauer, Liang Tong, Joshua J Woodward
An HD-domain phosphodiesterase mediates cooperative hydrolysis of c-di-AMP to affect bacterial growth and virulence.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2015, 112(7);E747-56
[PubMed:25583510]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Elodie Marchadier, Rut Carballido-López, Sophie Brinster, Céline Fabret, Peggy Mervelet, Philippe Bessières, Marie-Françoise Noirot-Gros, Vincent Fromion, Philippe Noirot
An expanded protein-protein interaction network in Bacillus subtilis reveals a group of hubs: Exploration by an integrative approach.
Proteomics: 2011, 11(15);2981-91
[PubMed:21630458]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)