Difference between revisions of "CheW"
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[CodY regulon]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[CodY regulon]]}}, | ||
| + | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[DegU regulon]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigD regulon]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[SigD regulon]]}}, | ||
{{SubtiWiki regulon|[[Spo0A regulon]]}} | {{SubtiWiki regulon|[[Spo0A regulon]]}} | ||
| Line 122: | Line 123: | ||
** [[CodY]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|12730172}} | ** [[CodY]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|12730172}} | ||
** [[DegU]] (non-phosphorylated): transcription activation {{PubMed|17850253}} | ** [[DegU]] (non-phosphorylated): transcription activation {{PubMed|17850253}} | ||
| + | ** [[DegU]]-P: transcription repression {{PubMed|24386445}} | ||
| + | ** [[DegU]]-P in complex with [[SwrA]]: transcription activation {{PubMed|24386445}} | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 153: | Line 156: | ||
<pubmed> 20122866 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 20122866 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>,8169224,1601874,14731274,1624415,14651647, 9657996,8157612,15175317 17850253 21098025 21515776</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>,8169224,1601874,14731274,1624415,14651647, 9657996,8157612,15175317 17850253 21098025 21515776 24386445</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 15:50, 29 December 2014
- Description: modulation of CheA activity in response to attractants, scaffold protein: facilitates coupling between CheA and receptors
| Gene name | cheW |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | CheA modulator |
| Function | control of CheA activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: cheW | |
| MW, pI | 17 kDa, 4.422 |
| Gene length, protein length | 468 bp, 156 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | cheA, cheC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 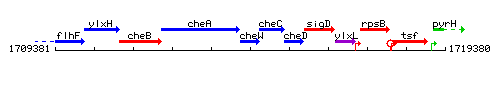
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CodY regulon, DegU regulon, SigD regulon, Spo0A regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16440
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16440
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): CheV (N-terminal domain)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
- predominantly present at the cell poles PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU16440
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39802
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- in minimal medium, CheW is present with 2,100 +/- 430 molecules per cell PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 840 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1423 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 1996 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 1296 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 699 PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Gerald L Hazelbauer, Wing-Cheung Lai
Bacterial chemoreceptors: providing enhanced features to two-component signaling.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2010, 13(2);124-32
[PubMed:20122866]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Original publications
Serena Mordini, Cecilia Osera, Simone Marini, Francesco Scavone, Riccardo Bellazzi, Alessandro Galizzi, Cinzia Calvio
The role of SwrA, DegU and P(D3) in fla/che expression in B. subtilis.
PLoS One: 2013, 8(12);e85065
[PubMed:24386445]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Vincent J Cannistraro, George D Glekas, Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
Cellular stoichiometry of the chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(13);3220-7
[PubMed:21515776]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kang Wu, Hanna E Walukiewicz, George D Glekas, George W Ordal, Christopher V Rao
Attractant binding induces distinct structural changes to the polar and lateral signaling clusters in Bacillus subtilis chemotaxis.
J Biol Chem: 2011, 286(4);2587-95
[PubMed:21098025]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kazuo Kobayashi
Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(2);395-409
[PubMed:17850253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Werhane, P Lopez, M Mendel, M Zimmer, G W Ordal, L M Márquez-Magaña
The last gene of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis, ylxL, is required for maximal sigmaD function.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(12);4025-9
[PubMed:15175317]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michael W Bunn, George W Ordal
Receptor conformational changes enhance methylesterase activity during chemotaxis by Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 51(3);721-8
[PubMed:14731274]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Patrick Eichenberger, José E González-Pastor, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 50(5);1683-701
[PubMed:14651647]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Estacio, S S Anna-Arriola, M Adedipe, L M Márquez-Magaña
Dual promoters are responsible for transcription initiation of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(14);3548-55
[PubMed:9657996]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Rosario, K L Fredrick, G W Ordal, J D Helmann
Chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis requires either of two functionally redundant CheW homologs.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(9);2736-9
[PubMed:8169224]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L M Márquez-Magaña, M J Chamberlin
Characterization of the sigD transcription unit of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(8);2427-34
[PubMed:8157612]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D W Hanlon, P B Carpenter, G W Ordal
Influence of attractants and repellents on methyl group turnover on methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins of Bacillus subtilis and role of CheW.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(13);4218-22
[PubMed:1624415]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D W Hanlon, L M Márquez-Magaña, P B Carpenter, M J Chamberlin, G W Ordal
Sequence and characterization of Bacillus subtilis CheW.
J Biol Chem: 1992, 267(17);12055-60
[PubMed:1601874]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)