Difference between revisions of "RpmE"
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU37070&redirect=T BSU37070] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/rpmE.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/rpmE.html] | ||
| Line 91: | Line 92: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU37070&redirect=T BSU37070] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
Revision as of 15:03, 2 April 2014
- Description: ribosomal protein
| Gene name | rpmE |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no PubMed |
| Product | ribosomal protein L31 |
| Function | translation |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rpmE | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RpmE | |
| MW, pI | 7 kDa, 9.157 |
| Gene length, protein length | 198 bp, 66 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | tdk, rho |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 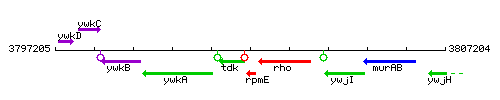
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed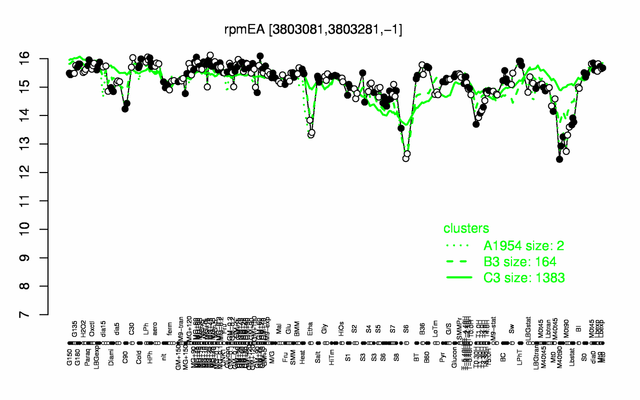
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37070
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37070
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: Type A subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): YtiA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: Zn(2+) PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU37070
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q03223
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Under conditions of zinc starvation, RpmE is replaced by its paralog YtiA, that does not require zinc PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon: rpmE PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Genki Akanuma, Hideaki Nanamiya, Yousuke Natori, Koichi Yano, Shota Suzuki, Shuya Omata, Morio Ishizuka, Yasuhiko Sekine, Fujio Kawamura
Inactivation of ribosomal protein genes in Bacillus subtilis reveals importance of each ribosomal protein for cell proliferation and cell differentiation.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(22);6282-91
[PubMed:23002217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hideaki Nanamiya, Fujio Kawamura
Towards an elucidation of the roles of the ribosome during different growth phases in Bacillus subtilis.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem: 2010, 74(3);451-61
[PubMed:20208344]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew A Lauber, William E Running, James P Reilly
B. subtilis ribosomal proteins: structural homology and post-translational modifications.
J Proteome Res: 2009, 8(9);4193-206
[PubMed:19653700]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Scott E Gabriel, John D Helmann
Contributions of Zur-controlled ribosomal proteins to growth under zinc starvation conditions.
J Bacteriol: 2009, 191(19);6116-22
[PubMed:19648245]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Yousuke Natori, Hideaki Nanamiya, Genki Akanuma, Saori Kosono, Toshiaki Kudo, Kozo Ochi, Fujio Kawamura
A fail-safe system for the ribosome under zinc-limiting conditions in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 63(1);294-307
[PubMed:17163968]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hideaki Nanamiya, Genki Akanuma, Yousuke Natori, Rikinori Murayama, Saori Kosono, Toshiaki Kudo, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara, Seung-Moon Park, Kozo Ochi, Fujio Kawamura
Zinc is a key factor in controlling alternation of two types of L31 protein in the Bacillus subtilis ribosome.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 52(1);273-83
[PubMed:15049826]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)