Difference between revisions of "GltA"
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU18450&redirect=T BSU18450] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/gltAB.html] | * '''DBTBS entry:''' [http://dbtbs.hgc.jp/COG/prom/gltAB.html] | ||
| Line 109: | Line 110: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU18450&redirect=T BSU18450] | ||
* '''Structure:''' [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2VDC 2VDC] (the [[GltA]]-[[GltB]] complex of ''Azospirillum brasiliense'') {{PubMed|18199747}} | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.pdb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2VDC 2VDC] (the [[GltA]]-[[GltB]] complex of ''Azospirillum brasiliense'') {{PubMed|18199747}} | ||
Revision as of 13:52, 2 April 2014
- Description: large subunit of glutamate synthase
| Gene name | gltA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glutamate synthase (large subunit) |
| Function | glutamate biosynthesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gltA | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GltA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: gltA | |
| MW, pI | 168 kDa, 5.47 |
| Gene length, protein length | 4560 bp, 1520 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | gltB, gltC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 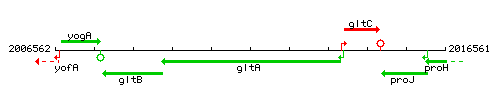
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed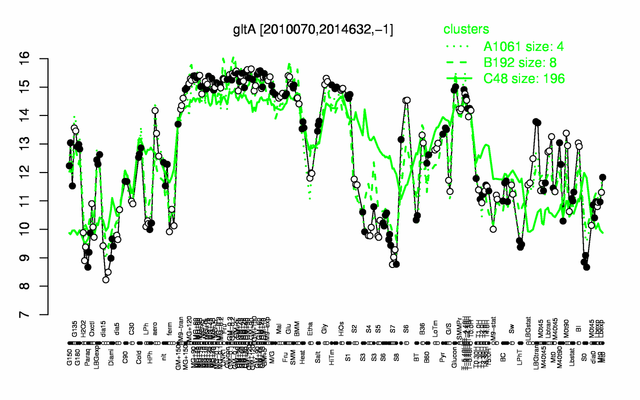
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
GltC regulon, FsrA regulon, TnrA regulon, Efp-dependent proteins
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU18450
Phenotypes of a mutant
auxotrophic for glutamate
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU18450
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 2 L-glutamate + NADP+ = L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH (according to Swiss-Prot) 2 L-glutamate + NADP(+) <=> L-glutamine + 2-oxoglutarate + NADPH
- Protein family: glutamate synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot) glutamate synthase family
- Paralogous protein(s): YerD
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Glutamine amidotransferase type-2 domain (22-415)
- Nucleotide binding domain (1060-1112)
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on Arg-904 AND/OR Arg-914 PubMed
- Cofactor(s): 3Fe-4S, FAD, FMN
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- membrane associated PubMed, cytoplasm
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU18450
- UniProt: P39812
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.4.1.13 3 1.4.1.13]
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- translation is likely to require Efp due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- expression activated by glucose (11 fold) (CcpA, GltC) PubMed
- repressed by arginine (GltC, RocG) PubMed
- expressed in the presence of ammonium PubMed
- repressed in the absence of good nitrogen sources (glutamine or ammonium) (TnrA) PubMed
- part of the iron sparing response, strong down-regulation in a fur mutant (Fur, FsrA) PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- translation is likely to require Efp due to the presence of several consecutive proline residues PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP807 (del gltAB::tet), GP222 (gltA under the control of p-xyl), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Fabian Commichau University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Alexander K W Elsholz, Kürsad Turgay, Stephan Michalik, Bernd Hessling, Katrin Gronau, Dan Oertel, Ulrike Mäder, Jörg Bernhardt, Dörte Becher, Michael Hecker, Ulf Gerth
Global impact of protein arginine phosphorylation on the physiology of Bacillus subtilis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(19);7451-6
[PubMed:22517742]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gregory T Smaldone, Olga Revelles, Ahmed Gaballa, Uwe Sauer, Haike Antelmann, John D Helmann
A global investigation of the Bacillus subtilis iron-sparing response identifies major changes in metabolism.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(10);2594-605
[PubMed:22389480]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Frederik M Meyer, Jan Gerwig, Elke Hammer, Christina Herzberg, Fabian M Commichau, Uwe Völker, Jörg Stülke
Physical interactions between tricarboxylic acid cycle enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for a metabolon.
Metab Eng: 2011, 13(1);18-27
[PubMed:20933603]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Katrin Gunka, Jens J Landmann, Jörg Stülke
Glutamate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: gene expression and enzyme activities evolved to avoid futile cycles and to allow rapid responses to perturbations of the system.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(10);3557-64
[PubMed:18326565]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Magali Cottevieille, Eric Larquet, Slavica Jonic, Maxim V Petoukhov, Gianluca Caprini, Stefano Paravisi, Dmitri I Svergun, Maria A Vanoni, Nicolas Boisset
The subnanometer resolution structure of the glutamate synthase 1.2-MDa hexamer by cryoelectron microscopy and its oligomerization behavior in solution: functional implications.
J Biol Chem: 2008, 283(13);8237-49
[PubMed:18199747]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ulf Gerth, Holger Kock, Ilja Kusters, Stephan Michalik, Robert L Switzer, Michael Hecker
Clp-dependent proteolysis down-regulates central metabolic pathways in glucose-starved Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(1);321-31
[PubMed:17981983]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Fabian M Commichau, Christina Herzberg, Philipp Tripal, Oliver Valerius, Jörg Stülke
A regulatory protein-protein interaction governs glutamate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis: the glutamate dehydrogenase RocG moonlights in controlling the transcription factor GltC.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 65(3);642-54
[PubMed:17608797]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Fabian M Commichau, Ingrid Wacker, Jan Schleider, Hans-Matti Blencke, Irene Reif, Philipp Tripal, Jörg Stülke
Characterization of Bacillus subtilis mutants with carbon source-independent glutamate biosynthesis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2007, 12(1-2);106-13
[PubMed:17183217]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Silvia Picossi, Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Molecular mechanism of the regulation of Bacillus subtilis gltAB expression by GltC.
J Mol Biol: 2007, 365(5);1298-313
[PubMed:17134717]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marcus Miethke, Helga Westers, Evert-Jan Blom, Oscar P Kuipers, Mohamed A Marahiel
Iron starvation triggers the stringent response and induces amino acid biosynthesis for bacillibactin production in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(24);8655-7
[PubMed:17012385]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Boris R Belitsky, Abraham L Sonenshein
Modulation of activity of Bacillus subtilis regulatory proteins GltC and TnrA by glutamate dehydrogenase.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(11);3399-407
[PubMed:15150225]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ingrid Wacker, Holger Ludwig, Irene Reif, Hans-Matti Blencke, Christian Detsch, Jörg Stülke
The regulatory link between carbon and nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the gltAB operon by the catabolite control protein CcpA.
Microbiology (Reading): 2003, 149(Pt 10);3001-3009
[PubMed:14523131]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ken-ichi Yoshida, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Masaki Kinehara, Yo-hei Ohki, Yoshiko Nakaura, Yasutaro Fujita
Identification of additional TnrA-regulated genes of Bacillus subtilis associated with a TnrA box.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 49(1);157-65
[PubMed:12823818]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B R Belitsky, L V Wray, S H Fisher, D E Bohannon, A L Sonenshein
Role of TnrA in nitrogen source-dependent repression of Bacillus subtilis glutamate synthase gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(21);5939-47
[PubMed:11029411]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
B R Belitsky, A L Sonenshein
Mutations in GltC that increase Bacillus subtilis gltA expression.
J Bacteriol: 1995, 177(19);5696-700
[PubMed:7559360]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D E Bohannon, A L Sonenshein
Positive regulation of glutamate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1989, 171(9);4718-27
[PubMed:2548995]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)