Difference between revisions of "EfeB"
(→Original publications) |
(→Original publications) |
||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
<pubmed> 24140208 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 24140208 </pubmed> | ||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
| − | <pubmed>16672620,19180538,12354229, 19383693 9353933 9683469 15554971 21479178 18179421 22923395 23180473 23560556 23764491 23820555 24620988 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>16672620,19180538,12354229, 19383693 9353933 9683469 15554971 21479178 18179421 22923395 23180473 23560556 23764491 23820555 24620988 18931290 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:41, 14 March 2014
- Description: elemental iron uptake system, heme peroxidase, converts ferrous iron (Fe(II) to ferric iron (FeIII)) for uptake by EfeO-EfeU, peroxide detoxification under microaerobic conditions
| Gene name | efeB |
| Synonyms | ipa-29d, ywbN |
| Essential | no |
| Product | heme peroxidase in elemental iron uptake |
| Function | ferrous iron conversion |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: efeB | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: EfeB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Protein secretion | |
| MW, pI | 45 kDa, 8.64 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1248 bp, 416 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywbO, efeO |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 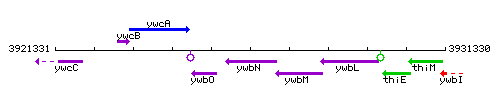
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
acquisition of iron, iron metabolism, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), resistance against oxidative and electrophile stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
Fur regulon, SigM regulon, SigW regulon, SigX regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38260
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: DyP-type peroxidase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P39597
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jan Maarten van Dijl, Groningen, Netherlands
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Ruihua Liu, Zhenqiang Zuo, Yingming Xu, Cunjiang Song, Hong Jiang, Chuanling Qiao, Ping Xu, Qixing Zhou, Chao Yang
Twin-arginine signal peptide of Bacillus subtilis YwbN can direct Tat-dependent secretion of methyl parathion hydrolase.
J Agric Food Chem: 2014, 62(13);2913-8
[PubMed:24620988]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ana Santos, Sónia Mendes, Vânia Brissos, Lígia O Martins
New dye-decolorizing peroxidases from Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas putida MET94: towards biotechnological applications.
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol: 2014, 98(5);2053-65
[PubMed:23820555]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Marcus Miethke, Carmine G Monteferrante, Mohamed A Marahiel, Jan Maarten van Dijl
The Bacillus subtilis EfeUOB transporter is essential for high-affinity acquisition of ferrous and ferric iron.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2013, 1833(10);2267-78
[PubMed:23764491]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Murat Sezer, Ana Santos, Patrycja Kielb, Tiago Pinto, Ligia O Martins, Smilja Todorovic
Distinct structural and redox properties of the heme active site in bacterial dye decolorizing peroxidase-type peroxidases from two subfamilies: resonance Raman and electrochemical study.
Biochemistry: 2013, 52(18);3074-84
[PubMed:23560556]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Carmine G Monteferrante, Calum MacKichan, Elodie Marchadier, Maria-Victoria Prejean, Rut Carballido-López, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Mapping the twin-arginine protein translocation network of Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2013, 13(5);800-11
[PubMed:23180473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Laxmi Krishnappa, Carmine G Monteferrante, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Degradation of the twin-arginine translocation substrate YwbN by extracytoplasmic proteases of Bacillus subtilis.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2012, 78(21);7801-4
[PubMed:22923395]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
René van der Ploeg, Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Marc Schaffer, Emma L Denham, Carmine G Monteferrante, Marcus Miethke, Mohamed A Marahiel, Colin R Harwood, Theresa Winter, Michael Hecker, Haike Antelmann, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Environmental salinity determines the specificity and need for Tat-dependent secretion of the YwbN protein in Bacillus subtilis.
PLoS One: 2011, 6(3);e18140
[PubMed:21479178]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Robyn T Eijlander, Magdalena A Kolbusz, Erwin M Berendsen, Oscar P Kuipers
Effects of altered TatC proteins on protein secretion efficiency via the twin-arginine translocation pathway of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 6);1776-1785
[PubMed:19383693]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Thijs R H M Kouwen, René van der Ploeg, Haike Antelmann, Michael Hecker, Georg Homuth, Ulrike Mäder, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Overflow of a hyper-produced secretory protein from the Bacillus Sec pathway into the Tat pathway for protein secretion as revealed by proteogenomics.
Proteomics: 2009, 9(4);1018-32
[PubMed:19180538]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Marc A B Kolkman, René van der Ploeg, Michael Bertels, Maurits van Dijk, Joop van der Laan, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Eugenio Ferrari
The twin-arginine signal peptide of Bacillus subtilis YwbN can direct either Tat- or Sec-dependent secretion of different cargo proteins: secretion of active subtilisin via the B. subtilis Tat pathway.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2008, 74(24);7507-13
[PubMed:18931290]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Warawan Eiamphungporn, John D Helmann
The Bacillus subtilis sigma(M) regulon and its contribution to cell envelope stress responses.
Mol Microbiol: 2008, 67(4);830-48
[PubMed:18179421]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Juliane Ollinger, Kyung-Bok Song, Haike Antelmann, Michael Hecker, John D Helmann
Role of the Fur regulon in iron transport in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(10);3664-73
[PubMed:16672620]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jan D H Jongbloed, Ulrike Grieger, Haike Antelmann, Michael Hecker, Reindert Nijland, Sierd Bron, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Two minimal Tat translocases in Bacillus.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 54(5);1319-25
[PubMed:15554971]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Noel Baichoo, Tao Wang, Rick Ye, John D Helmann
Global analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Fur regulon and the iron starvation stimulon.
Mol Microbiol: 2002, 45(6);1613-29
[PubMed:12354229]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Huang, K L Fredrick, J D Helmann
Promoter recognition by Bacillus subtilis sigmaW: autoregulation and partial overlap with the sigmaX regulon.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(15);3765-70
[PubMed:9683469]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
E Presecan, I Moszer, L Boursier, H Cruz Ramos, V de la Fuente, M-F Hullo, C Lelong, S Schleich, A Sekowska, B H Song, G Villani, F Kunst, A Danchin, P Glaser
The Bacillus subtilis genome from gerBC (311 degrees) to licR (334 degrees).
Microbiology (Reading): 1997, 143 ( Pt 10);3313-3328
[PubMed:9353933]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)