Difference between revisions of "FbaA"
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
{{SubtiWiki category|[[carbon core metabolism]]}}, | {{SubtiWiki category|[[carbon core metabolism]]}}, | ||
| − | {{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphoproteins]]}} | + | {{SubtiWiki category|[[phosphoproteins]]}}, |
| + | [[most abundant proteins]] | ||
= This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | = This gene is a member of the following [[regulons]] = | ||
| Line 126: | Line 127: | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
** The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation {{PubMed|20525796}} | ** The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation {{PubMed|20525796}} | ||
| + | ** belongs to the 100 [[most abundant proteins]] {{PubMed|15378759}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| Line 151: | Line 153: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>17218307, 15125960, 24624 16843441 11489127 20525796 23420519 23033921 24571712</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>17218307, 15125960, 24624 16843441 11489127 20525796 23420519 23033921 24571712 15378759</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 5 March 2014
- Description: fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme
| Gene name | fbaA |
| Synonyms | fba, fba1, tsr |
| Essential | no |
| Product | fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: fbaA | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: fbaA | |
| MW, pI | 30,2 kDa, 5.03 |
| Gene length, protein length | 855 bp, 285 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | ywjH, spo0F |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 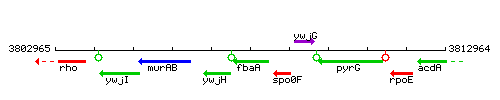
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
carbon core metabolism, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU37120
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: D-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate = glycerone phosphate + D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: class II fructose-bisphosphate aldolase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): FbaB
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- 2 x Dihydroxyacetone phosphate binding domain (210–212), (231–234)
- Modification: phosphorylation on Thr-212 and Thr-234 PubMed
- Cofactors: Zn2+ (Metalloenzyme)
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- Structure: 3Q94 (from Bacillus anthracis)
- UniProt: P13243
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.1.2.13
Additional information
- Binds 2 zinc ions per subunit. One is catalytic and the other provides a structural contribution
- extensive information on the structure and enzymatic properties of FbaA can be found at Proteopedia
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- The mRNA has a long 5' leader region. This may indicate RNA-based regulation PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- GP591 (fbaA::cat), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- GP596 (fbaA::erm), available in Jörg Stülke's lab, PubMed
- Expression vector:
- for expression in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP1423, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression/ purification from B. subtilis with N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, in pGP380: pGP88, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- for expression/ purification from E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP395, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- lacZ fusion: pGP601 (in pAC6)
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References