Difference between revisions of "YfnI"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
* induction of [[SigM]] and [[SigX]] activities {{PubMed|23103977}} | * induction of [[SigM]] and [[SigX]] activities {{PubMed|23103977}} | ||
| + | * more sensitive to nisin {{PubMed|23980836}} | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 143: | Line 144: | ||
<pubmed> 21388439 21255102</pubmed> | <pubmed> 21388439 21255102</pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>17434969, 18957862 17218307 19229300 21255105, 23103977</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>17434969, 18957862 17218307 19229300 21255105, 23103977 23980836</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 30 August 2013
- Description: polyglycerolphosphate lipoteichoic acid synthase, general stress protein, major secreted protein, required for survival at low temperature (4°C)
| Gene name | yfnI |
| Synonyms | yetP, ltaSA |
| Essential | no |
| Product | minor lipoteichoic acid synthetase |
| Function | biosynthesis of lipoteichoic acid |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: yfnI | |
| MW, pI | 73 kDa, 5.951 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1917 bp, 639 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yetO, yfnH |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 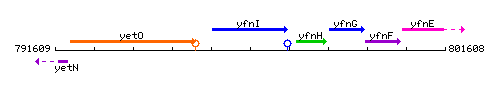
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell wall synthesis, biosynthesis of cell wall components, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, V, W, X, Y), phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU07260
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: LTA synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on (Thr-311 OR Ser-312) PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
- extracellular (signal peptide) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q797B3
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: yfnI (according to DBTBS)
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- SM-NB (yfnI-spc), available in Anne Galinier's and Boris Görke's labs
- GP1390 yfnI::spc, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- GP1397 yfnI::ermC, available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications