Difference between revisions of "ResD"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[resE]]'', ''[[resC]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[resE]]'', ''[[resC]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU23120 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU23120 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU23120 | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU23120 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU23120 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU23120 DNA_with_flanks] |
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 10:36, 14 May 2013
- Description: two-component response regulator, regulation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Gene name | resD |
| Synonyms | ypxD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component response regulator |
| Function | regulation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration respiration |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: resD | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: ResD | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Nucleotides (regulation), Central C-metabolism, Stress, Alternative nitrogen sources | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 5.631 |
| Gene length, protein length | 720 bp, 240 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | resE, resC |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 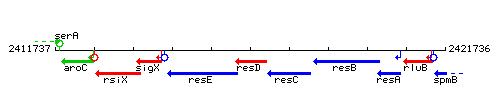
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
regulators of electron transport, transcription factors and their control, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
CcpA regulon, PhoP regulon, ResD regulon
The ResD regulon
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23120
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: OmpR family of two-component response regulators
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylated by ResE on an Asp residue
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: phosphorylation likely affects DNA-binding activity
- Interactions:
- ResD interacts with the RNA polymerase PubMed
- ResE-ResD
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P35163
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Marion Hulett, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Additional publications: PubMed
Sushma Kommineni, Amrita Lama, Benjamin Popescu, Michiko M Nakano
Global transcriptional control by NsrR in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(7);1679-88
[PubMed:22287527]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Sushma Kommineni, Erik Yukl, Takahiro Hayashi, Jacob Delepine, Hao Geng, Pierre Moënne-Loccoz, Michiko M Nakano
Nitric oxide-sensitive and -insensitive interaction of Bacillus subtilis NsrR with a ResDE-controlled promoter.
Mol Microbiol: 2010, 78(5);1280-93
[PubMed:21091510]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ankita Puri-Taneja, Matthew Schau, Yinghua Chen, F Marion Hulett
Regulators of the Bacillus subtilis cydABCD operon: identification of a negative regulator, CcpA, and a positive regulator, ResD.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(9);3348-58
[PubMed:17322317]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Michiko M Nakano, Hao Geng, Shunji Nakano, Kazuo Kobayashi
The nitric oxide-responsive regulator NsrR controls ResDE-dependent gene expression.
J Bacteriol: 2006, 188(16);5878-87
[PubMed:16885456]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Elisabeth Härtig, Anja Hartmann, Manuela Schätzle, Alessandra M Albertini, Dieter Jahn
The Bacillus subtilis nrdEF genes, encoding a class Ib ribonucleotide reductase, are essential for aerobic and anaerobic growth.
Appl Environ Microbiol: 2006, 72(8);5260-5
[PubMed:16885274]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Soo-Keun Choi, Milton H Saier
Mechanism of CcpA-mediated glucose repression of the resABCDE operon of Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2006, 11(1-2);104-10
[PubMed:16825793]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Matthew Schau, Amr Eldakak, F Marion Hulett
Terminal oxidases are essential to bypass the requirement for ResD for full Pho induction in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(24);8424-32
[PubMed:15576792]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Paul, X Zhang, F M Hulett
Two ResD-controlled promoters regulate ctaA expression in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(10);3237-46
[PubMed:11325953]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y Zhu
Involvement of ResE phosphatase activity in down-regulation of ResD-controlled genes in Bacillus subtilis during aerobic growth.
J Bacteriol: 2001, 183(6);1938-44
[PubMed:11222591]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
X Zhang, F M Hulett
ResD signal transduction regulator of aerobic respiration in Bacillus subtilis: ctaA promoter regulation.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 37(5);1208-19
[PubMed:10972837]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y Zhu, M Lacelle, X Zhang, F M Hulett
Interaction of ResD with regulatory regions of anaerobically induced genes in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 37(5);1198-207
[PubMed:10972836]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Fabret, V A Feher, J A Hoch
Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(7);1975-83
[PubMed:10094672]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S M Birkey, W Liu, X Zhang, M F Duggan, F M Hulett
Pho signal transduction network reveals direct transcriptional regulation of one two-component system by another two-component regulator: Bacillus subtilis PhoP directly regulates production of ResD.
Mol Microbiol: 1998, 30(5);943-53
[PubMed:9988472]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, Y P Dailly, P Zuber, D P Clark
Characterization of anaerobic fermentative growth of Bacillus subtilis: identification of fermentation end products and genes required for growth.
J Bacteriol: 1997, 179(21);6749-55
[PubMed:9352926]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M M Nakano, P Zuber, P Glaser, A Danchin, F M Hulett
Two-component regulatory proteins ResD-ResE are required for transcriptional activation of fnr upon oxygen limitation in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(13);3796-802
[PubMed:8682783]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Sun, E Sharkova, R Chesnut, S Birkey, M F Duggan, A Sorokin, P Pujic, S D Ehrlich, F M Hulett
Regulators of aerobic and anaerobic respiration in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(5);1374-85
[PubMed:8631715]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)