Difference between revisions of "PtsG"
(→Original publications) |
|||
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
<pubmed> 18086213 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 18086213 </pubmed> | ||
==Original publications== | ==Original publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>10627040 ,12850135 ,18763711 ,11902727 ,9765562 ,9513271 ,1956301 ,10543968 ,17074746 ,15155854 ,14527945 ,1508157 ,2120236 9593197 8418852 1581296 1316146 1733770 1942043 1911744 1906345 20081037 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>10627040 ,12850135 ,18763711 ,11902727 ,9765562 ,9513271 ,1956301 ,10543968 ,17074746 ,15155854 ,14527945 ,1508157 ,2120236 9593197 8418852 1581296 1316146 1733770 1942043 1911744 1906345 20081037 22846916 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 09:03, 1 August 2012
- Description: trigger enzyme: major glucose permease of the PTS, EIICBA(Glc) and control of GlcT activity
| Gene name | ptsG |
| Synonyms | ptsX, crr |
| Essential | no |
| Product | trigger enzyme: glucose-specific enzyme IICBA component of the PTS |
| Function | glucose transport and phosphorylation, control of GlcT activity |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: PtsG | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism, Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 75,3 kDa, 5.40 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2097 bp, 699 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | glcT, ptsH |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 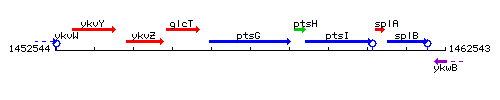
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed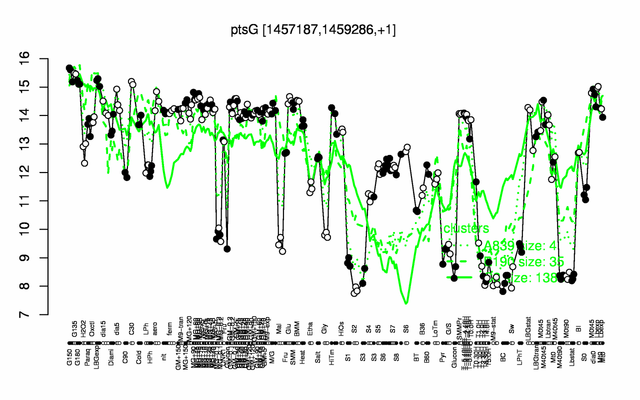
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
phosphotransferase systems, carbon core metabolism, transcription factors and their control, trigger enzyme, membrane proteins, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
GlcT regulon, stringent response
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13890
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transport and phosphorylation of glucose, receives a phosphate from HPr at the IIA domain (His-620), the phosphate group is then transferred to the IIB domain (Cys-461) an finally to the incoming glucose. In the absence of glucose, PtsG phosphorylates and thereby inactivates the transcriptional antiterminator GlcT.
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- 11x transmembrane domain (16–36, 89–109, 139–159, 180–200, 233–253, 283–303, 313–333, 338–358, 365–385, 388–408)
- PTS EIIC domain ( 1-424)
- PTS EIIB domain (439–520)
- PTS EIIA domain (568–672)
- Modification: transient phosphorylation (HPr-dependent) on His-620, then internal phosphotransfer from His-620 to Cys-461
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: membrane protein PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P20166
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.1.69
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- transcriptional antitermination via the GlcT-dependent RNA switch PubMed
- stringent response: due to presence of guanine at +1 position of the transcript PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutants: all available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- pGP34 (pAC5), available in Stülke lab
- pGP66 (pAC7), available in Stülke lab
- pGP606 (mutant terminator, pAC6), available in Stülke lab
- pGP532 (pAC7), available in Stülke lab
- series of promoter deletions are available in pAC5 and pAC6, available in Stülke lab
- series of RAT mutants are available in pAC6, available in Stülke lab
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original publications
Natividad Cabrera-Valladares, Luz M Martínez, Noemí Flores, Georgina Hernández-Chávez, Alfredo Martínez, Francisco Bolívar, Guillermo Gosset
Physiologic consequences of glucose transport and phosphoenolpyruvate node modifications in Bacillus subtilis 168.
J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol: 2012, 22(3);177-97
[PubMed:22846916]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Shigeo Tojo, Kanako Kumamoto, Kazutake Hirooka, Yasutaro Fujita
Heavy involvement of stringent transcription control depending on the adenine or guanine species of the transcription initiation site in glucose and pyruvate metabolism in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(6);1573-85
[PubMed:20081037]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Oliver Schilling, Christina Herzberg, Tina Hertrich, Hanna Vörsmann, Dirk Jessen, Sebastian Hübner, Fritz Titgemeyer, Jörg Stülke
Keeping signals straight in transcription regulation: specificity determinants for the interaction of a family of conserved bacterial RNA-protein couples.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2006, 34(21);6102-15
[PubMed:17074746]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Oliver Schilling, Ines Langbein, Michael Müller, Matthias H Schmalisch, Jörg Stülke
A protein-dependent riboswitch controlling ptsGHI operon expression in Bacillus subtilis: RNA structure rather than sequence provides interaction specificity.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2004, 32(9);2853-64
[PubMed:15155854]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I e)
Matthias H Schmalisch, Steffi Bachem, Jörg Stülke
Control of the Bacillus subtilis antiterminator protein GlcT by phosphorylation. Elucidation of the phosphorylation chain leading to inactivation of GlcT.
J Biol Chem: 2003, 278(51);51108-15
[PubMed:14527945]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hans-Matti Blencke, Georg Homuth, Holger Ludwig, Ulrike Mäder, Michael Hecker, Jörg Stülke
Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways.
Metab Eng: 2003, 5(2);133-49
[PubMed:12850135]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jonathan Reizer, Steffi Bachem, Aiala Reizer, Maryvonne Arnaud, Milton H Saier, Jörg Stülke
Novel phosphotransferase system genes revealed by genome analysis - the complete complement of PTS proteins encoded within the genome of Bacillus subtilis.
Microbiology (Reading): 1999, 145 ( Pt 12);3419-3429
[PubMed:10627040]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
I Langbein, S Bachem, J Stülke
Specific interaction of the RNA-binding domain of the bacillus subtilis transcriptional antiterminator GlcT with its RNA target, RAT.
J Mol Biol: 1999, 293(4);795-805
[PubMed:10543968]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Bachem, J Stülke
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis GlcT antiterminator protein by components of the phosphotransferase system.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(20);5319-26
[PubMed:9765562]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Chen, D A Case, J Reizer, M H Saier, P E Wright
High-resolution solution structure of Bacillus subtilis IIAglc.
Proteins: 1998, 31(3);258-70
[PubMed:9593197]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)
S Bachem, N Faires, J Stülke
Characterization of the presumptive phosphorylation sites of the Bacillus subtilis glucose permease by site-directed mutagenesis: implication in glucose transport and catabolite repression.
FEMS Microbiol Lett: 1997, 156(2);233-8
[PubMed:9513271]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Stülke, I Martin-Verstraete, M Zagorec, M Rose, A Klier, G Rapoport
Induction of the Bacillus subtilis ptsGHI operon by glucose is controlled by a novel antiterminator, GlcT.
Mol Microbiol: 1997, 25(1);65-78
[PubMed:11902727]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Y Chen, J Reizer, M H Saier, W J Fairbrother, P E Wright
Mapping of the binding interfaces of the proteins of the bacterial phosphotransferase system, HPr and IIAglc.
Biochemistry: 1993, 32(1);32-7
[PubMed:8418852]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Zagorec, P W Postma
Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the ptsG gene of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Gen Genet: 1992, 234(2);325-8
[PubMed:1508157]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W J Fairbrother, A G Palmer, M Rance, J Reizer, M H Saier, P E Wright
Assignment of the aliphatic 1H and 13C resonances of the Bacillus subtilis glucose permease IIA domain using double- and triple-resonance heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy.
Biochemistry: 1992, 31(18);4413-25
[PubMed:1581296]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M J Stone, W J Fairbrother, A G Palmer, J Reizer, M H Saier, P E Wright
Backbone dynamics of the Bacillus subtilis glucose permease IIA domain determined from 15N NMR relaxation measurements.
Biochemistry: 1992, 31(18);4394-406
[PubMed:1316146]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W J Fairbrother, G P Gippert, J Reizer, M H Saier, P E Wright
Low resolution solution structure of the Bacillus subtilis glucose permease IIA domain derived from heteronuclear three-dimensional NMR spectroscopy.
FEBS Lett: 1992, 296(2);148-52
[PubMed:1733770]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Kapadia, C C Chen, P Reddy, M H Saier, J Reizer, O Herzberg
Crystallization of the IIA domain of the glucose permease of Bacillus subtilis.
J Mol Biol: 1991, 221(4);1079-80
[PubMed:1942043]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D I Liao, G Kapadia, P Reddy, M H Saier, J Reizer, O Herzberg
Structure of the IIA domain of the glucose permease of Bacillus subtilis at 2.2-A resolution.
Biochemistry: 1991, 30(40);9583-94
[PubMed:1911744]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W J Fairbrother, J Cavanagh, H J Dyson, A G Palmer, S L Sutrina, J Reizer, M H Saier, P E Wright
Polypeptide backbone resonance assignments and secondary structure of Bacillus subtilis enzyme IIIglc determined by two-dimensional and three-dimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy.
Biochemistry: 1991, 30(28);6896-907
[PubMed:1906345]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Gonzy-Tréboul, J H de Waard, M Zagorec, P W Postma
The glucose permease of the phosphotransferase system of Bacillus subtilis: evidence for IIGlc and IIIGlc domains.
Mol Microbiol: 1991, 5(5);1241-9
[PubMed:1956301]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S L Sutrina, P Reddy, M H Saier, J Reizer
The glucose permease of Bacillus subtilis is a single polypeptide chain that functions to energize the sucrose permease.
J Biol Chem: 1990, 265(30);18581-9
[PubMed:2120236]
[WorldCat.org]
(P p)