Difference between revisions of "GlnR"
(→Reviews) |
(→Reviews) |
||
| Line 152: | Line 152: | ||
<big>''Gunka K, Commichau FM'' </big> | <big>''Gunka K, Commichau FM'' </big> | ||
<big>'''Control of glutamate homeostasis in ''Bacillus subtilis'':''' </big> | <big>'''Control of glutamate homeostasis in ''Bacillus subtilis'':''' </big> | ||
| − | <big>'''a complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, glutamate biosynthesis and degradation. ''' </big> | + | <big>'''a complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, ''' </big> |
| + | <big>'''glutamate biosynthesis and degradation. ''' </big> | ||
<big>Mol Microbiol.: 2012, 85(2) 213-224. </big> | <big>Mol Microbiol.: 2012, 85(2) 213-224. </big> | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22625175 PubMed:22625175] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22625175 PubMed:22625175] | ||
Revision as of 17:47, 6 July 2012
| Gene name | glnR |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcription repressor |
| Function | regulation of glutamine synthesis |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: GlnR | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Ammonium/ glutamate, Cell wall, Alternative nitrogen sources | |
| MW, pI | 15 kDa, 9.731 |
| Gene length, protein length | 405 bp, 135 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ynbB, glnA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 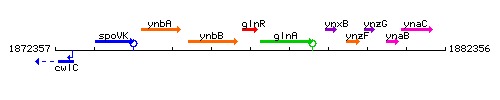
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, glutamate metabolism, transcription factors and their control
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The GlnR regulon:
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU17450
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity: activity is enhanced upon interaction of the C-terminal domain with GlnA PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P37582
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Susan Fisher, Boston, USA homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Gunka K, Commichau FM Control of glutamate homeostasis in Bacillus subtilis: a complex interplay between ammonium assimilation, glutamate biosynthesis and degradation. Mol Microbiol.: 2012, 85(2) 213-224. PubMed:22625175
Original publications