Difference between revisions of "PtsH"
(→Extended information on the protein) |
|||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
* '''Domains:''' HPr Domain (2–88) | * '''Domains:''' HPr Domain (2–88) | ||
| − | * '''Modification:''' phosphorylation | + | * '''Modification:''' phosphorylations: transient phosphorylation by [[PtsI |Enzyme I]] of the PTS on His-15, regulatory phosphorylation on Ser-46 by [[HprK]], weak phosphorylation on Ser-12 |
* '''Cofactor(s):''' | * '''Cofactor(s):''' | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 13 January 2009
- Description: HPr, General component of the sugar phosphotransferase system (PTS).
| Gene name | ptsH |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | histidine-containing phosphocarrier protein HPr of the PTS |
| Function | PTS-dependent sugar trnasport and carbon catabolite repression |
| MW, pI | 9,1 kDa, 4.58 |
| Gene length, protein length | 264 bp, 88 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | ptsG, ptsI |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 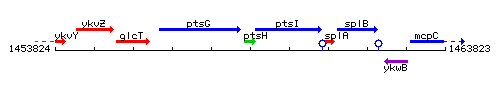
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates: 1458693 - 1458956
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry:[2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Protein HPr N(pi)-phospho-L-histidine + protein EIIA = protein HPr + protein EIIA N(tau)-phospho-L-histidine
- Protein family: HPr family
- Paralogous protein(s): Crh
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains: HPr Domain (2–88)
- Modification: phosphorylations: transient phosphorylation by Enzyme I of the PTS on His-15, regulatory phosphorylation on Ser-46 by HprK, weak phosphorylation on Ser-12
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions: GapA-HPr PubMed, HPr-MtlR, HPr-LicR, HPr-LevR,HPr-ManR, YesS-HPr (HPr-His-P), HPr-CcpA PubMed, HPr-RbsR PubMed, HprK-HPr PubMed
- Localization: Cytoplasm
Database entries
- Structure: NCBI, complex of L. Casei HprK with B. Subtilis HPr NCBI, complex of L. Casei HprK with B. Subtilis HPr-Ser-P NCBI
- Swiss prot entry: [3]
- KEGG entry: [4]
- E.C. number: [5]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
Labs working on this gene/protein
Josef Deutscher, Paris-Grignon, France
Jörg Stülke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Wolfgang Hillen, Erlangen University, Germany Homepage
Richard Brennan, Houston, Texas, USA Homepage
Boris Görke, University of Göttingen, Germany Homepage
Anne Galinier, University of Marseille, France
Your additional remarks
References
- Macek B, Mijakovic I, Olsen JV (2007) The serine/threonine/tyrosine phosphoproteome of the model bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(4): 697-707. PubMed
- Müller W, Horstmann N, Hillen W (2006) The transcription regulator RbsR represents a novel interaction partner of the phosphoprotein HPr-Ser46-P in Bacillus subtilis FEBS J. 273(6): 1251-61. PubMed
- Pompeo et al. (2007) Interaction of GapA with HPr and its homologue, Crh: Novel levels of regulation of a key step of glycolysis in Bacillus subtilis? J Bacteriol 189, 1154-1157.PubMed
1. Arnaud M, Vary P, Zagorec M, Klier A, Débarbouillé M, Postma P, Rapoport G (1992) Regulation of the sacPA operon of Bacillus subtilis: identification of phosphotransferase system components involved in SacT activity. J Bacteriol 174:3161-3170 2. Deutscher, J., Kessler, U., Alpert, C. A., and Hengstenberg, W. (1984) Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system: P-ser-HPr and its possible regulatory function. Biochemistry 23: 4455-4460. 3. Deutscher, J., Küster, E., Bergstedt, U., Charrier, V., and Hillen, W. 1995. Protein kinase-dependent HPr/CcpA interaction links glycolytic activity to carbon catabolite repression in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 15: 1049-1053. 4. Eisermann, R., Deutscher, J., Gonzy-Tréboul, G., and Hengstenberg, W. (1988) Site-directed mutagenesis with the ptsH gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 263: 17050-17054. 5. Frisby, D., and Zuber, P. 1994. Mutations in pts cause catabolite-resistant sporulation and altered regulation of spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 176: 2587-2595. 6. Galinier A, Deutscher J, Martin-Verstraete I: Phosphorylation of either Crh or HPr mediates binding of CcpA to the Bacillus subtilis xyn cre and catabolite repression of the xyn operon. J Mol Biol 1999, 286:307-314. 7. Görke, B., Fraysse, L. & Galinier, A. Drastic differences in Crh and HPr synthesis levels reflect their different impacts on catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 186, 2992-2995 (2004). 8. Lindner, C., Galinier, A., Hecker, M. & Deutscher, J. Regulation of the activity of the Bacillus subtilis antiterminator LicT by multiple PEP-dependent, enzyme I- and HPr-catalysed phosphorylation. Mol. Microbiol. 31, 995-1006 (1999). 9. Lindner, C., Hecker, M., Le Coq, D. & Deutscher, J. Bacillus subtilis mutant LicT antiterminators exhibiting enzyme I- and HPr-independent antitermination affect catabolite repression of the bglPH operon. J. Bacteriol. 184, 4819-4828 (2002). 10. Martin-Verstraete, I., Charrier, V., Stülke, J., Galinier, A., Erni, B., Rapoport, G., & Deutscher, J. (1998) Antagonistic effects of dual PTS catalyzed phosphorylation on the Bacillus subtilis transcriptional activator LevR. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 293-303. 11. Martin-Verstraete, I., Deutscher, J., and Galinier, A. (1999) Phosphorylation of HPr and Crh by HprK, early steps in the catabolite repression signalling pathway for the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon. J Bacteriol 181: 2966-2969. 12. Reizer, J., Sutrina, S. L., Saier, Jr., M. H., Stewart, G. C., Peterkofsky, A., and Reddy, P. (1989) Mechanistic and physiological consequences of HPr(Ser) phosphorylation on the activities of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in Gram-positive bacteria: studies with site-specific mutants of HPr. EMBO J 8: 2111-2120. 13. Schmalisch, M., Bachem, S. & Stülke, J. (2003) Control of the Bacillus subtilis antiterminator protein GlcT by phosphorylation: Elucidation of the phosphorylation chain leading to inactivation of GlcT. J. Biol. Chem. 278: 51108-51115. 14. Schumacher, M. A. et al. Structural basis for allosteric control of the transcription regulator CcpA by the phosphoprotein HPr-Ser46-P. Cell 118, 731-741 (2004). 15. Singh, K. D., Halbedel, S., Görke, B. & Stülke, J. (2007) Control of the phosphorylation state of the HPr protein of the phosphotransferase system in Bacillus subtilis: implication of the protein phosphatase PrpC. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 13: 165-171. 16. Singh, K. D., Schmalisch, M. H., Stülke, J. & Görke, B. (2008) Carbon catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis: A quantitative analysis of repression exerted by different carbon sources. J. Bacteriol. 190: 7275-7284. 17. Stülke, J., Martin-Verstraete, I., Charrier, V., Klier, A., Deutscher, J. & Rapoport, G. (1995) The HPr protein of the phosphotransferase system links induction and catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon. J. Bacteriol. 177: 6928-6936. 18. Tortosa, P., Aymerich, S., Lindner, C., Saier, M.H., Jr., Reizer, J. and Le Coq, D. (1997) Multiple phosphorylation of SacY, a Bacillus subtilis antiterminator negatively controlled by the phosphotransferase system. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 17230-17237.