Difference between revisions of "MinC"
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
* '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' | ||
** ''[[radC]]'': [[SigM]] {{PubMed|18179421}} | ** ''[[radC]]'': [[SigM]] {{PubMed|18179421}} | ||
| − | |||
** ''[[minC]]'': [[SigH]] {{PubMed|8459776}} | ** ''[[minC]]'': [[SigH]] {{PubMed|8459776}} | ||
| Line 139: | Line 138: | ||
<pubmed> 19680248 19884039 </pubmed> | <pubmed> 19680248 19884039 </pubmed> | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>8459776,19019154,1400224,10411726,15317782, 20352045,18588879, 19141479 20566861 20711458 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>8459776,19019154,1400224,10411726,15317782, 20352045,18588879, 19141479 20566861 20711458 18179421</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 16:10, 17 May 2011
- Description: cell-division inhibitor (septum placement), destabilizes FtsZ-rings at new cell poles
| Gene name | minC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | cell-division inhibitor |
| Function | septum placement |
| MW, pI | 24 kDa, 6.262 |
| Gene length, protein length | 678 bp, 226 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | minD, mreD |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 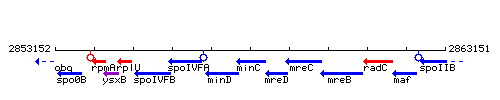
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y), membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28000
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: The Min system prevents minicell formation adjacent to recently completed division sites by promoting the disassembly of the cytokinetic ring, thereby ensuring that cell division occurs only once per cell cycle PubMed
- Protein family: minC family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q01463
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications