Difference between revisions of "MreB"
(→Expression and regulation) |
(→Expression and regulation) |
||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
** ''[[radC]]-[[mreB]]-[[mreC]]-[[mreD]]-[[minC]]-[[minD]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18179421 PubMed] | ** ''[[radC]]-[[mreB]]-[[mreC]]-[[mreD]]-[[minC]]-[[minD]]'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/18179421 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' [[SigH]] {{PubMed|8459776}} | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
| + | ** ''[[mreB]]: [[SigH]] {{PubMed|8459776}} | ||
| + | ** ''[[radC]]: [[SigM]] {{PubMed|18179421}} | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
Revision as of 15:31, 17 May 2011
- Description: cell-shape determining protein, forms filaments
| Gene name | mreB |
| Synonyms | divIVB |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-shape determining protein |
| Function | cell-shape determination |
| MW, pI | 35 kDa, 4.901 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1011 bp, 337 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mreC, radC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 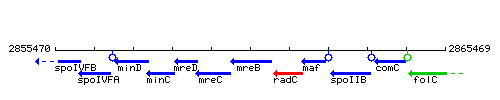
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell shape, cell envelope stress proteins (controlled by SigM, W, X, Y), essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU28030
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed, the mutation can be suppressed by inactivation of ponA, ptsI, ccpA PubMed, by overexpression of YvcK PubMed, or by addition of 5 mM magnesium to the growth medium PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: ftsA/mreB family (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: Q01465
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in the labs of Jeff Errington and Boris Görke
- Antibody: available in the Jeff Errington and Peter Graumann labs
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jeff Errington, Newcastle University, UK homepage
Peter Graumann, Freiburg University, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Additional reviews: PubMed
Peter L Graumann
Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2007, 61;589-618
[PubMed:17506674]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Rut Carballido-López
The bacterial actin-like cytoskeleton.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2006, 70(4);888-909
[PubMed:17158703]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Linda A Amos, Fusinita van den Ent, Jan Löwe
Structural/functional homology between the bacterial and eukaryotic cytoskeletons.
Curr Opin Cell Biol: 2004, 16(1);24-31
[PubMed:15037301]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Localization
Other original publications