Difference between revisions of "AlsD"
(→Biological materials) |
|||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| − | ** induction by acetate ([[AlsR]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7685336 PubMed] | + | ** induction by acetate ([[AlsR]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7685336 PubMed] |
| − | ** | + | ** repressed as long as terminal electron acceptors are available for respiration ([[Rex]]) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16428414 PubMed] |
| − | Note: since acetate formation requires ''[[ackA]]'' activation by [[CcpA]] there is an indirect effect of [[CcpA]] on the '' | + | ** subject to positive stringent control upon lysine starvation {{PubMed|20081037}} |
| + | |||
| + | Note: since acetate formation requires ''[[ackA]]'' activation by [[CcpA]] there is an indirect effect of [[CcpA]] on the ''alsSD'' operon: the operon is not expressed in ''[[ccpA]]'' mutants | ||
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' | ||
| + | ** stringent response: due to presence of adenines at +1 and +2 positions of the transcript {{PubMed|20081037}} | ||
** [[AlsR]]: transcription activation in the presence of acetate [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7685336 PubMed] | ** [[AlsR]]: transcription activation in the presence of acetate [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/7685336 PubMed] | ||
** [[Rex]]: transcription repression if the ratio NADH2/NAD is high [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16428414 PubMed] | ** [[Rex]]: transcription repression if the ratio NADH2/NAD is high [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/16428414 PubMed] | ||
| Line 127: | Line 130: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>19087206,10986270,,16428414,16493705 7685336 16428414, </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>19087206,10986270,,16428414,16493705 7685336 16428414, 20081037 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 17:14, 19 January 2010
- Description: acetolactate decarboxylase
| Gene name | alsD |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetolactate decarboxylase) |
| Function | overflow metabolism |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 28 kDa, 4.603 |
| Gene length, protein length | 765 bp, 255 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywrO, alsS |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 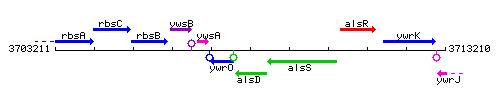
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36000
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: (2S)-2-hydroxy-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate = (3R)-3-hydroxybutan-2-one + CO2 (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylated on ser/ thr/ tyr PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: Q04777
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 4.1.1.5
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
Note: since acetate formation requires ackA activation by CcpA there is an indirect effect of CcpA on the alsSD operon: the operon is not expressed in ccpA mutants
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References