Difference between revisions of "GuaB"
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/PMID PubMed] | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/PMID PubMed] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 08:05, 21 July 2009
- Description: IMP dehydrogenase
| Gene name | guaB |
| Synonyms | guaA |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | IMP dehydrogenase |
| Function | biosynthesis of GMP |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Purine synthesis, Nucleotides (regulation) | |
| MW, pI | 52 kDa, 6.168 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1464 bp, 488 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yaaC, dacA |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 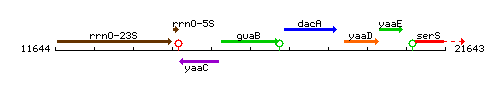
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU00090
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Inosine 5'-phosphate + NAD+ + H2O = xanthosine 5'-phosphate + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: IMPDH/GMPR family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylated (STY) PubMed, S-cysteinlyation after diamide stress (Cys-308) PubMed, PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P21879
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.1.1.205
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: guaB
- Regulation:
- Additional information: the mRNA is very stable (half-life > 15 min) PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Christine Eymann, Dörte Becher, Jörg Bernhardt, Katrin Gronau, Anja Klutzny, Michael Hecker
Dynamics of protein phosphorylation on Ser/Thr/Tyr in Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(19);3509-26
[PubMed:17726680]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Falko Hochgräfe, Jörg Mostertz, Dierk-Christoph Pöther, Dörte Becher, John D Helmann, Michael Hecker
S-cysteinylation is a general mechanism for thiol protection of Bacillus subtilis proteins after oxidative stress.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(36);25981-5
[PubMed:17611193]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
G Hambraeus, C von Wachenfeldt, L Hederstedt
Genome-wide survey of mRNA half-lives in Bacillus subtilis identifies extremely stable mRNAs.
Mol Genet Genomics: 2003, 269(5);706-14
[PubMed:12884008]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Yoshiko Nakaura, Robert P Shivers, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Richard Losick, Yasutaro Fujita, Abraham L Sonenshein
Additional targets of the Bacillus subtilis global regulator CodY identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation and genome-wide transcript analysis.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(6);1911-22
[PubMed:12618455]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H H Saxild, P Nygaard
Regulation of levels of purine biosynthetic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: effects of changing purine nucleotide pools.
J Gen Microbiol: 1991, 137(10);2387-94
[PubMed:1722815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J M Lopez, A Dromerick, E Freese
Response of guanosine 5'-triphosphate concentration to nutritional changes and its significance for Bacillus subtilis sporulation.
J Bacteriol: 1981, 146(2);605-13
[PubMed:6111556]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)