Difference between revisions of "GbsA"
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
* '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P71016 P71016] | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P71016 P71016] | ||
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu:BSU31060] |
* '''E.C. number:''' [http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/1.2.1.8 1.2.1.8] | * '''E.C. number:''' [http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/1.2.1.8 1.2.1.8] | ||
Revision as of 02:21, 25 June 2009
- Description: glycine betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase, glycine betaine synthesis
| Gene name | gbsA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glycine betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| Function | osmoprotection |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Stress | |
| MW, pI | 53 kDa, 4.713 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1470 bp, 490 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | gbsB, yuaC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 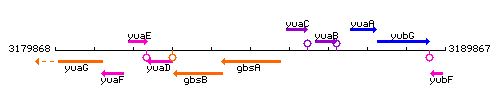
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU31060
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Betaine aldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = betaine + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: aldehyde dehydrogenase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P71016
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 1.2.1.8
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Erhard Bremer, University of Marburg, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
J Boch, G Nau-Wagner, S Kneip, E Bremer
Glycine betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis: characterization of an enzyme required for the synthesis of the osmoprotectant glycine betaine.
Arch Microbiol: 1997, 168(4);282-9
[PubMed:9297465]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
J Boch, B Kempf, R Schmid, E Bremer
Synthesis of the osmoprotectant glycine betaine in Bacillus subtilis: characterization of the gbsAB genes.
J Bacteriol: 1996, 178(17);5121-9
[PubMed:8752328]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)