Difference between revisions of "Tpi"
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
* '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27876 P27876] | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P27876 P27876] | ||
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' [http://www.genome.jp/dbget-bin/www_bget?bsu:BSU33920] |
* '''E.C. number:''' [http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/5.3.1.1 5.3.1.1] 5.3.1.1] | * '''E.C. number:''' [http://www.expasy.org/enzyme/5.3.1.1 5.3.1.1] 5.3.1.1] | ||
Revision as of 05:04, 25 June 2009
- Description: triose phosphate isomerase, glycolytic/ gluconeogenic enzyme
| Gene name | tpi |
| Synonyms | tpiA |
| Essential | yes |
| Product | triosephosphate isomerase |
| Function | enzyme in glycolysis/ gluconeogenesis |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism, Sugar catabolism | |
| MW, pI | 26,9 kDa, 4.79 |
| Gene length, protein length | 759 bp, 253 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | pgk, pgm |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 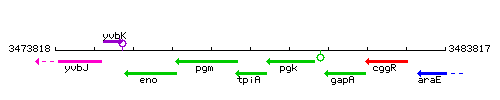
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU33920
Phenotypes of a mutant
- Essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate = dihydroxyacetone phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: triosephosphate isomerase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification: phosphorylation on Ser-213 PubMed
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: inhibited by 2-phosphoglycolate (in B. stearothermophilus) PubMed
- Interactions:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot), cytoplasm PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 1BTM (complex with 2-phosphoglycolic acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus), complex with 2-phosphpoglycolic acid, Geobacillus stearothermophilus NCBI
- Swiss prot entry: P27876
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 5.3.1.1 5.3.1.1]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulation: expression activated by glucose (2.8 fold) PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector: pGP394 (N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844), pGP89 (N-terminal Strep-tag, for SPINE, expression in B. subtilis), available in Stülke lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system: B. pertussis adenylate cyclase-based bacterial two hybrid system (BACTH), available in Stülke lab
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References