Difference between revisions of "ResD"
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>8631715,11222591,9988472, </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>8682783,15576792,16885274,16885456,11325953,10094672,17322317,8631715,9988472,10972837,10972836,9352926,,8631715,11222591,9988472, </pubmed> |
# Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | # Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title ''Journal'' '''volume:''' page-page. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/PMID PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 08:35, 14 June 2009
- Description: two-component response regulator, regulation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration
| Gene name | resD |
| Synonyms | ypxD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | two-component response regulator |
| Function | regulation of aerobic and anaerobic respiration respiration (resA, ctaA, qcrABC, fnr, lctEP) |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism, Stress | |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 5.631 |
| Gene length, protein length | 720 bp, 240 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | resE, resC |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 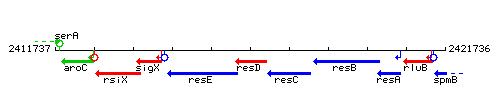
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU23120
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: OmpR family of two-component response regulators
- Paralogous protein(s):
Genes/ operons regulated by ResD
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- Swiss prot entry: P35163
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Marion Hulett, University of Illinois at Chicago, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed