Difference between revisions of "CggR"
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
* '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]] | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]] | ||
| − | * '''Regulation:''' [[CggR]] represses the operon in the absence of glycolytic sugars [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+12622823 PubMed] | + | * '''Regulation:''' expression activated by glucose (76.76) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12850135 PubMed], [[CggR]] represses the operon in the absence of glycolytic sugars [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=+12622823 PubMed] |
* '''Regulatory mechanism:''' repression | * '''Regulatory mechanism:''' repression | ||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| + | # Blencke et al. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in ''Bacillus subtilis'': regulation of the central metabolic pathways. ''Metab Eng.'' '''5:''' 133-149 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12850135 PubMed] | ||
# Commichau, F. M., Rothe, F. M., Herzberg, C., Wagner, E., Hellwig, D., Lehnik-Habrink, M., Hammer, E., Völker, U. & Stülke, J. Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: Interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing. subm. | # Commichau, F. M., Rothe, F. M., Herzberg, C., Wagner, E., Hellwig, D., Lehnik-Habrink, M., Hammer, E., Völker, U. & Stülke, J. Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: Interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing. subm. | ||
# Doan, T., and S. Aymerich. 2003. Regulation of the central glycolytic pathways in Bacillus subtilis: binding of the repressor CggR to its single DNA target sequence is modulated by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Mol. Microbiol. 47: 1709-1721. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12622823 PubMed] | # Doan, T., and S. Aymerich. 2003. Regulation of the central glycolytic pathways in Bacillus subtilis: binding of the repressor CggR to its single DNA target sequence is modulated by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Mol. Microbiol. 47: 1709-1721. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/12622823 PubMed] | ||
Revision as of 23:08, 1 April 2009
- Description: repressor of the glycolytic gapA operon
| Gene name | cggR |
| Synonyms | yvbQ |
| Essential | no |
| Product | central glycolytic genes regulator |
| Function | transcriptional regulator |
| MW, pI | 37,2 kDa,5.68 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1020 bp, 340 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | araE, gapA |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
Genetic context 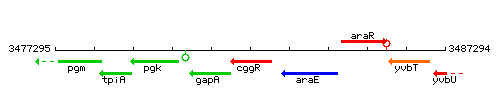
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates: 3481786 - 3482805
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: transcription repression of the glycolytic gapA operon
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- DNA binding domain (H-T-H motif) (37–56)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity: fructose 1.6-bisphosphate PubMed and dihydroxyacetone phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate PubMed act as inducer and result in release of CggR from the DNA
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Swiss prot entry: [3]
- KEGG entry: [4]
Additional information
Expression and regulation
The primary mRNAs of the operon are highly unstable. The primary mRNA is subject to processing at the very end of the cggR open reading frame. This results in stable mature gapA and gapA-pgk-tpiA-pgm-eno mRNAs. The processing event requires the Rny protein.
- Sigma factor: SigA
- Regulation: expression activated by glucose (76.76) PubMed, CggR represses the operon in the absence of glycolytic sugars PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism: repression
- Database entries: DBTBS
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP311 (in frame deletion), available in Stülke lab
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody: available in Stülke lab
Labs working on this gene/protein
Stephane Aymerich, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Your additional remarks
References
- Blencke et al. (2003) Transcriptional profiling of gene expression in response to glucose in Bacillus subtilis: regulation of the central metabolic pathways. Metab Eng. 5: 133-149 PubMed
- Commichau, F. M., Rothe, F. M., Herzberg, C., Wagner, E., Hellwig, D., Lehnik-Habrink, M., Hammer, E., Völker, U. & Stülke, J. Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: Interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing. subm.
- Doan, T., and S. Aymerich. 2003. Regulation of the central glycolytic pathways in Bacillus subtilis: binding of the repressor CggR to its single DNA target sequence is modulated by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Mol. Microbiol. 47: 1709-1721. PubMed
- Doan et al. (2008) A phospho-sugar binding domain homologous to NagB enzymes regulates the activity of the central glycolytic genes repressor. Proteins 71:2038-2050. PubMed
- Fillinger, S., Boschi-Muller, S., Azza, S., Dervyn, E., Branlant, G., and Aymerich, S. (2000) Two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases with opposite physiological roles in a nonphotosynthetic bacterium. J Biol Chem 275, 14031-14037. PubMed
- Ludwig, H., Homuth, G., Schmalisch, M., Dyka, F. M., Hecker, M., and Stülke, J. (2001) Transcription of glycolytic genes and operons in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for the presence of multiple levels of control of the gapA operon. Mol Microbiol 41, 409-422.PubMed
- Ludwig, H., Rebhan, N., Blencke, H.-M., Merzbacher, M. & Stülke, J. (2002). Control of the glycolytic gapA operon by the catabolite control protein A in Bacillus subtilis: a novel mechanism of CcpA-mediated regulation. Mol Microbiol 45, 543-553.PubMed
- Meinken, C., Blencke, H. M., Ludwig, H., and Stülke, J. (2003) Expression of the glycolytic gapA operon in Bacillus subtilis: differential synthesis of proteins encoded by the operon. Microbiology 149, 751-761. PubMed
- Rezacova et al. (2008) Crystal structures of the effector-binding domain of repressor Central glycolytic gene Regulator from Bacillus subtilis reveal ligand-induced structural changes upon binding of several glycolytic intermediates. Mol. Microbiol. 69:895-910. PubMed
- Zorilla et al. (2007) Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate acts both as an inducer and as a structural cofactor of the central glycolytic genes repressor (CggR). Biochemistry 46:14996-15008. PubMed
- Zorilla et al. (2007) Inducer-modulated cooperative binding of the tetrameric CggR repressor to operator DNA. Biophys. J. 92: 3215-3227. PubMed