Difference between revisions of "MreC"
(→Expression and regulation) |
Mark Leaver (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== Basic information === | === Basic information === | ||
| − | * '''Coordinates:''' | + | * '''Coordinates:''' 2859062-2859931 |
===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ===Phenotypes of a mutant === | ||
| − | essential [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12682299 PubMed] | + | ''mreC'' is essential under normal conditions [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12682299 PubMed]. Depletion of MreC leads to a progressive increse in the width and a decreas in the length of the cell. This shape defect is consistent with a role for ''mreC'' in cell wall synthesis during elongation and similar to other genes with roles in elongation like [[rodA]] and the redundant gene pair [[pbpA]] and pbpH (also known as [[ykuA]]). Electron microscopy of cells depleted of MreC show regions of the cell where a thick and irregular cell wall has accumulated [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12867458 PubMed] and [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16101995 PubMed]. ''mreC'' can be deleted provided that 0.5 M sucrose and 20 mM Magnesium is provided in the media, ''mreC'' is therefore conditionally essentail. The phenotype of the ''mreC'' deletion in these conditions is one characterised by extreamly fat and bloated cells that tend to grow in clusters [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16101995 PubMed]. |
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
=== Extended information on the protein === | === Extended information on the protein === | ||
| − | * '''Kinetic information:''' | + | * '''Kinetic information:''' None |
| − | * '''Domains:''' | + | * '''Domains:''' Intracellular N-terminus, transmembrane domain, Coiled coil domain and C-terminal beta-sheet domain. |
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
| − | * '''Interactions:''' | + | * '''Interactions:''' Interacts with MreD, and a subset of the PBPs [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17427287 PubMed] |
| − | * '''Localization:''' | + | * '''Localization:''' GFP-MreC localises to the cell membrane in a helical pattern [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16101995 PubMed]. |
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:-''' |
| + | ** 2J5U: MreC from ''Lysteria monocytogenes'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17427287 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** 2QF4: MreC monomer from ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17707860 PubMed] | ||
| + | ** 2QF5: MreC dimer from ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17707860 PubMed] | ||
| − | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' | + | * '''Swiss prot entry:''' Q01466 |
| − | * '''KEGG entry:''' | + | * '''KEGG entry:''' K03570 |
* '''E.C. number:''' | * '''E.C. number:''' | ||
| Line 92: | Line 95: | ||
=Expression and regulation= | =Expression and regulation= | ||
| − | * '''Operon:''' | + | * '''Operon:''' mreB-'''mreC'''-mreD-minC-minD |
* '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigH]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8459776 PubMed] | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigH]] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/8459776 PubMed] | ||
| Line 104: | Line 107: | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | * '''Mutant:''' | + | * '''Mutant:''' A non-polar inframe deletion strain named 3481 and a xylose dependent conditional mutant named 3461 is avaliable from the [[Errington]] lab [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16101995 PubMed]. |
* '''Expression vector:''' | * '''Expression vector:''' | ||
| Line 110: | Line 113: | ||
* '''lacZ fusion:''' | * '''lacZ fusion:''' | ||
| − | * '''GFP fusion:''' | + | * '''GFP fusion:''' |
* '''two-hybrid system:''' | * '''two-hybrid system:''' | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 6 March 2009
- Description: write here
| Gene name | mreC |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | cell-shape determining protein |
| Function | |
| MW, pI | 32 kDa, 6.248 |
| Gene length, protein length | 870 bp, 290 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mreD, mreB |
| Gene sequence (+200bp) | Protein sequence |
| Caution: The sequence for this gene in SubtiList contains errors | |
Genetic context 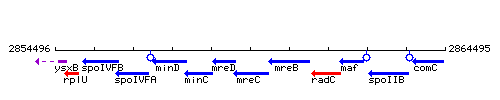
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Coordinates: 2859062-2859931
Phenotypes of a mutant
mreC is essential under normal conditions PubMed. Depletion of MreC leads to a progressive increse in the width and a decreas in the length of the cell. This shape defect is consistent with a role for mreC in cell wall synthesis during elongation and similar to other genes with roles in elongation like rodA and the redundant gene pair pbpA and pbpH (also known as ykuA). Electron microscopy of cells depleted of MreC show regions of the cell where a thick and irregular cell wall has accumulated PubMed and PubMed. mreC can be deleted provided that 0.5 M sucrose and 20 mM Magnesium is provided in the media, mreC is therefore conditionally essentail. The phenotype of the mreC deletion in these conditions is one characterised by extreamly fat and bloated cells that tend to grow in clusters PubMed.
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: None
- Domains: Intracellular N-terminus, transmembrane domain, Coiled coil domain and C-terminal beta-sheet domain.
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions: Interacts with MreD, and a subset of the PBPs PubMed
- Localization: GFP-MreC localises to the cell membrane in a helical pattern PubMed.
Database entries
- Structure:-
- Swiss prot entry: Q01466
- KEGG entry: K03570
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: mreB-mreC-mreD-minC-minD
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: A non-polar inframe deletion strain named 3481 and a xylose dependent conditional mutant named 3461 is avaliable from the Errington lab PubMed.
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
- Author1, Author2 & Author3 (year) Title Journal volume: page-page. PubMed