Difference between revisions of "MetE"
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 10685 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 10685 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1682 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ** number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1682 {{PubMed|24696501}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9230 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4809 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
| + | ** number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3703 {{PubMed|21395229}} | ||
=Biological materials = | =Biological materials = | ||
| − | |||
* '''Mutant:''' | * '''Mutant:''' | ||
** 1A607 ( ''metE''::''erm''), {{PubMed|3015878}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A607&Search=1A607 BGSC] | ** 1A607 ( ''metE''::''erm''), {{PubMed|3015878}}, available at [http://pasture.asc.ohio-state.edu/BGSC/getdetail.cfm?bgscid=1A607&Search=1A607 BGSC] | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 17 April 2014
- Description: methionine synthase
| Gene name | metE |
| Synonyms | metC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | methionine synthase |
| Function | biosynthesis of methionine |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: metE | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MetE | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: metE | |
| MW, pI | 86 kDa, 4.839 |
| Gene length, protein length | 2286 bp, 762 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | guaD, ispA |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 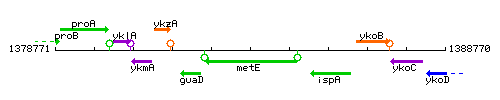
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed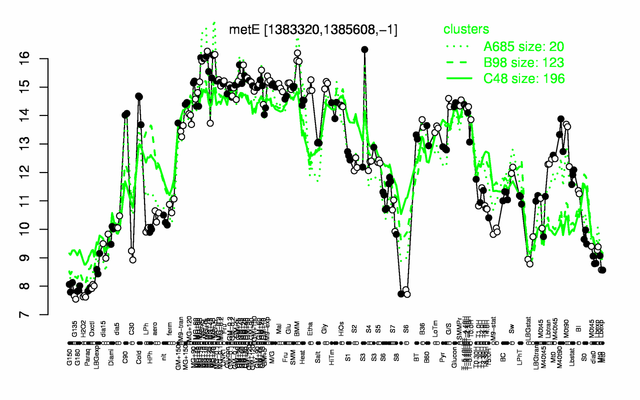
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
biosynthesis/ acquisition of amino acids, phosphoproteins, most abundant proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU13180
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13180
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: 5-methyltetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate + L-homocysteine = tetrahydropteroyltri-L-glutamate + L-methionine (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: vitamin-B12 independent methionine synthase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- phosphorylated on ser/ thr/ tyr PubMed, S-cysteinylation after diamide stress (C719) PubMed
- Cys719 and Cys730 are S-bacillithiolated by NaOCl stress in B. subtilis and other Bacillus species PubMed PubMed
- MetE is generally most strongly S-bacillithiolated by NaOCl stress in B. subtilis and other Bacillus species PubMed PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU13180
- UniProt: P80877
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number: 2.1.1.14
Additional information
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
Expression and regulation
- Operon: metE
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism: S-box: transcription termination/ antitermination, the S-box riboswitch binds S-adenosylmethionine resulting in termination PubMed
- Additional information:
- subject to Clp-dependent proteolysis upon glucose starvation PubMed
- belongs to the 100 most abundant proteins PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium): 10685 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (complex medium with amino acids, without glucose): 1682 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, exponential phase): 9230 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, early stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 4809 PubMed
- number of protein molecules per cell (minimal medium with glucose and ammonium, late stationary phase after glucose exhaustion): 3703 PubMed
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References