Difference between revisions of "KtrB"
(→Expression and regulation) |
|||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU31100&redirect=T BSU31100] | ||
* '''DBTBS entry:''' no entry | * '''DBTBS entry:''' no entry | ||
| Line 98: | Line 99: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| + | * '''BsubCyc:''' [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/NEW-IMAGE?type=NIL&object=BSU31100&redirect=T BSU31100] | ||
* '''Structure:''' | * '''Structure:''' | ||
Revision as of 14:36, 2 April 2014
| Gene name | ktrB |
| Synonyms | yubG |
| Essential | no |
| Product | high affinity potassium transporter KtrA-KtrB, integral membrane subunit (proton symport) |
| Function | potassium uptake |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: ktrB | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: KtrB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Metal ion homeostasis, ktrB | |
| MW, pI | 48 kDa, 10.116 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1335 bp, 445 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ktrA, yubF |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 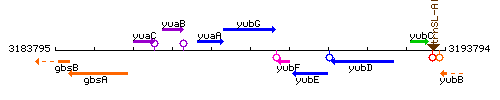
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transporters/ other, metal ion homeostasis (K, Na, Ca, Mg), coping with hyper-osmotic stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU31100
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU31100
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s): KtrD
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Modification:
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: integral membrane protein PubMed
Database entries
- BsubCyc: BSU31100
- UniProt: O32081
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- expression is controlled via termination antitermination by the ydaO riboswitch, expression is switched off upon binding od c-di-AMP PubMed
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- 1A954 ( ktrB::kan), PubMed, available at BGSC
- GHB1 (D(ktrA-ktrB)::aphA3), available in Erhard Bremer's lab
- GP92 (D(ktrA-ktrB)::aphA3), available in Jörg Stülke's lab
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Erhard Bremer, University of Marburg, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
James W Nelson, Narasimhan Sudarsan, Kazuhiro Furukawa, Zasha Weinberg, Joy X Wang, Ronald R Breaker
Riboswitches in eubacteria sense the second messenger c-di-AMP.
Nat Chem Biol: 2013, 9(12);834-9
[PubMed:24141192]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ricardo S Vieira-Pires, Andras Szollosi, João H Morais-Cabral
The structure of the KtrAB potassium transporter.
Nature: 2013, 496(7445);323-8
[PubMed:23598340]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Peter Y Watson, Martha J Fedor
The ydaO motif is an ATP-sensing riboswitch in Bacillus subtilis.
Nat Chem Biol: 2012, 8(12);963-5
[PubMed:23086297]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Kirsten F Block, Ming C Hammond, Ronald R Breaker
Evidence for widespread gene control function by the ydaO riboswitch candidate.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(15);3983-9
[PubMed:20511502]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ronald A Albright, Kyu Joh, João H Morais-Cabral
Probing the structure of the dimeric KtrB membrane protein.
J Biol Chem: 2007, 282(48);35046-55
[PubMed:17932047]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ronald A Albright, José-Luís Vazquez Ibar, Chae Un Kim, Sol M Gruner, João Henrique Morais-Cabral
The RCK domain of the KtrAB K+ transporter: multiple conformations of an octameric ring.
Cell: 2006, 126(6);1147-59
[PubMed:16990138]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Gudrun Holtmann, Evert P Bakker, Nobuyuki Uozumi, Erhard Bremer
KtrAB and KtrCD: two K+ uptake systems in Bacillus subtilis and their role in adaptation to hypertonicity.
J Bacteriol: 2003, 185(4);1289-98
[PubMed:12562800]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)