Difference between revisions of "RasP"
(→References) |
(→Reviews) |
||
| Line 145: | Line 145: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
==Reviews== | ==Reviews== | ||
| − | <pubmed> 20836086 23479438,22381678 22688815 </pubmed> | + | <pubmed> 20836086 23479438,22381678 22688815 19189971 </pubmed> |
| + | |||
== Original publications == | == Original publications == | ||
<pubmed>16899079,15130127,18599827,17020588,19889088 ,18763711, 20644139 21810987 23687273 23155385</pubmed> | <pubmed>16899079,15130127,18599827,17020588,19889088 ,18763711, 20644139 21810987 23687273 23155385</pubmed> | ||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 13:56, 31 July 2013
- Description: intramembrane protease, cleaves FtsL, RsiV and RsiW as well as signal peptides after release of the secreted proteins
| Gene name | rasP |
| Synonyms | yluC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | intramembrane protease |
| Function | control of cell division, and SigV and SigW activity |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: rasP | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: RasP | |
| MW, pI | 46 kDa, 5.14 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1266 bp, 422 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ispC, proS |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 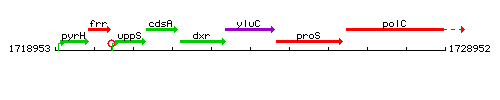
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
cell division, proteolysis, sigma factors and their control, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16560
Phenotypes of a mutant
- defects in competence development, protein secretion and membrane protein production PubMed
- mutants grow slower in liquid, are not competent, can’t activate SigW, have cell division defects, and decreased long term survival PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: no entry
- SubtiList entry: [1]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: peptidase M50B family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O31754
- KEGG entry: [2]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Thomas Wiegert, University of Bayreuth, Germany Homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Noël Molière, Kürşad Turgay
General and regulatory proteolysis in Bacillus subtilis.
Subcell Biochem: 2013, 66;73-103
[PubMed:23479438]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Ross E Dalbey, Peng Wang, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Membrane proteases in the bacterial protein secretion and quality control pathway.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(2);311-30
[PubMed:22688815]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Theresa D Ho, Craig D Ellermeier
Extra cytoplasmic function σ factor activation.
Curr Opin Microbiol: 2012, 15(2);182-8
[PubMed:22381678]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Gu Chen, Xu Zhang
New insights into S2P signaling cascades: regulation, variation, and conservation.
Protein Sci: 2010, 19(11);2015-30
[PubMed:20836086]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Michael S Wolfe
Intramembrane-cleaving proteases.
J Biol Chem: 2009, 284(21);13969-73
[PubMed:19189971]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications
Jessica L Hastie, Kyle B Williams, Craig D Ellermeier
The activity of σV, an extracytoplasmic function σ factor of Bacillus subtilis, is controlled by regulated proteolysis of the anti-σ factor RsiV.
J Bacteriol: 2013, 195(14);3135-44
[PubMed:23687273]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Jessica C Zweers, Pierre Nicolas, Thomas Wiegert, Jan Maarten van Dijl, Emma L Denham
Definition of the σ(W) regulon of Bacillus subtilis in the absence of stress.
PLoS One: 2012, 7(11);e48471
[PubMed:23155385]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Akira Saito, Yohei Hizukuri, Ei-ichi Matsuo, Shinobu Chiba, Hiroyuki Mori, Osamu Nishimura, Koreaki Ito, Yoshinori Akiyama
Post-liberation cleavage of signal peptides is catalyzed by the site-2 protease (S2P) in bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2011, 108(33);13740-5
[PubMed:21810987]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Inga Wadenpohl, Marc Bramkamp
DivIC stabilizes FtsL against RasP cleavage.
J Bacteriol: 2010, 192(19);5260-3
[PubMed:20644139]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Janine Heinrich, Kerstin Hein, Thomas Wiegert
Two proteolytic modules are involved in regulated intramembrane proteolysis of Bacillus subtilis RsiW.
Mol Microbiol: 2009, 74(6);1412-26
[PubMed:19889088]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hannes Hahne, Susanne Wolff, Michael Hecker, Dörte Becher
From complementarity to comprehensiveness--targeting the membrane proteome of growing Bacillus subtilis by divergent approaches.
Proteomics: 2008, 8(19);4123-36
[PubMed:18763711]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Janine Heinrich, Tuula Lundén, Vesa P Kontinen, Thomas Wiegert
The Bacillus subtilis ABC transporter EcsAB influences intramembrane proteolysis through RasP.
Microbiology (Reading): 2008, 154(Pt 7);1989-1997
[PubMed:18599827]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Marc Bramkamp, Louise Weston, Richard A Daniel, Jeff Errington
Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of FtsL protein and the control of cell division in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 62(2);580-91
[PubMed:17020588]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Stephan Zellmeier, Wolfgang Schumann, Thomas Wiegert
Involvement of Clp protease activity in modulating the Bacillus subtilissigmaw stress response.
Mol Microbiol: 2006, 61(6);1569-82
[PubMed:16899079]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Susanne Schöbel, Stephan Zellmeier, Wolfgang Schumann, Thomas Wiegert
The Bacillus subtilis sigmaW anti-sigma factor RsiW is degraded by intramembrane proteolysis through YluC.
Mol Microbiol: 2004, 52(4);1091-105
[PubMed:15130127]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)