Difference between revisions of "GapB"
(→References) |
(→Extended information on the protein) |
||
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
* '''Modification:''' | * '''Modification:''' | ||
| − | * '''Cofactor(s):''' NADP (preferentially) and NAD [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10799476 PubMed] | + | * '''Cofactor(s):''' NADP<sup>+</sup> (preferentially) and NAD<sup>+</sup> [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/10799476 PubMed] |
* '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | * '''Effectors of protein activity:''' | ||
Revision as of 08:03, 27 August 2013
- Description: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, NADP-dependent, gluconeogenic enzyme, forms a transhydrogenation cycle with GapA for balancing of NADPH
| Gene name | gapB |
| Synonyms | ppc |
| Essential | no |
| Product | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2 |
| Function | anabolic enzyme in gluconeogenesis |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: gapB | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Cys, Met & Sulfate assimilation, Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 37,3 kDa, 6.47 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1020 bp, 340 amino acids |
| Immediate neighbours | speD, ytcD |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 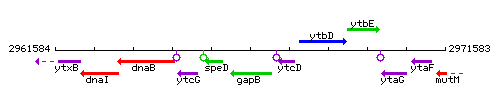
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed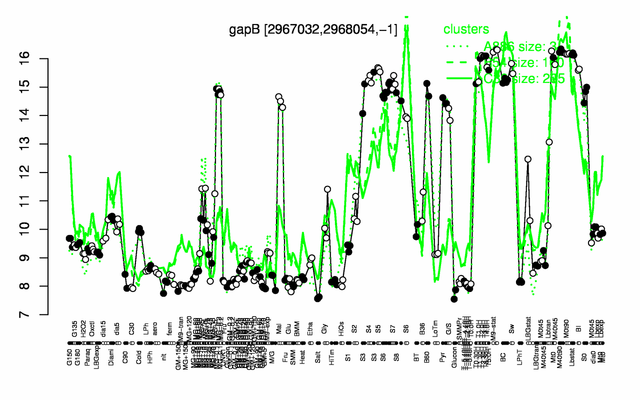
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29020
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD(P)+ = 3-phospho-D-glyceroyl phosphate + NAD(P)H (according to Swiss-Prot)
- This reaction is part of the gluconeogenesis
- Protein family: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s): GapA
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information: Michaelis-Menten PubMed
- Domains:
- Nucleotid bindinge domain (12-13)
- 2x Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate binding domain (151-153) & (210-211)
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): NADP+ (preferentially) and NAD+ PubMed
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: Cytoplasm (Homogeneous) PubMed
Database entries
- Structure: 3PRL (from B. halodurans)
- UniProt: O34425
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.2.1.59
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Stephane Aymerich, Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, INRA Paris-Grignon, France
Your additional remarks
References
Imke G de Jong, Jan-Willem Veening, Oscar P Kuipers
Single cell analysis of gene expression patterns during carbon starvation in Bacillus subtilis reveals large phenotypic variation.
Environ Microbiol: 2012, 14(12);3110-21
[PubMed:23033921]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Martin Rühl, Dominique Le Coq, Stéphane Aymerich, Uwe Sauer
13C-flux analysis reveals NADPH-balancing transhydrogenation cycles in stationary phase of nitrogen-starving Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 2012, 287(33);27959-70
[PubMed:22740702]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Matthew L Ferguson, Dominique Le Coq, Matthieu Jules, Stéphane Aymerich, Ovidiu Radulescu, Nathalie Declerck, Catherine A Royer
Reconciling molecular regulatory mechanisms with noise patterns of bacterial metabolic promoters in induced and repressed states.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2012, 109(1);155-60
[PubMed:22190493]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Simon Tännler, Eliane Fischer, Dominique Le Coq, Thierry Doan, Emmanuel Jamet, Uwe Sauer, Stéphane Aymerich
CcpN controls central carbon fluxes in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2008, 190(18);6178-87
[PubMed:18586936]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Helena B Thomaides, Ella J Davison, Lisa Burston, Hazel Johnson, David R Brown, Alison C Hunt, Jeffery Errington, Lloyd Czaplewski
Essential bacterial functions encoded by gene pairs.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(2);591-602
[PubMed:17114254]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Jean-Christophe Meile, Ling Juan Wu, S Dusko Ehrlich, Jeff Errington, Philippe Noirot
Systematic localisation of proteins fused to the green fluorescent protein in Bacillus subtilis: identification of new proteins at the DNA replication factory.
Proteomics: 2006, 6(7);2135-46
[PubMed:16479537]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Pascale Servant, Dominique Le Coq, Stéphane Aymerich
CcpN (YqzB), a novel regulator for CcpA-independent catabolite repression of Bacillus subtilis gluconeogenic genes.
Mol Microbiol: 2005, 55(5);1435-51
[PubMed:15720552]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
A Sekowska, J Y Coppée, J P Le Caer, I Martin-Verstraete, A Danchin
S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase of Bacillus subtilis is closely related to archaebacterial counterparts.
Mol Microbiol: 2000, 36(5);1135-47
[PubMed:10844697]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Fillinger, S Boschi-Muller, S Azza, E Dervyn, G Branlant, S Aymerich
Two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases with opposite physiological roles in a nonphotosynthetic bacterium.
J Biol Chem: 2000, 275(19);14031-7
[PubMed:10799476]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)