Difference between revisions of "MscL"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU36360 mscL] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU36360 mscL] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/ | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/subtipathways/search.php?enzyme=mscL mscL]''' |
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 14 kDa, 4.649 | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"| '''MW, pI''' || 14 kDa, 4.649 | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 7 January 2014
- Description: large conductance mechanosensitive channel protein, prevents selective release of cytoplasmic proteins in a hypotonic environment
| Gene name | mscL |
| Synonyms | ywpC |
| Essential | no |
| Product | large conductance mechanosensitive channel protein |
| Function | resistance to osmotic downshockglycine betaine export |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mscL | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: mscL | |
| MW, pI | 14 kDa, 4.649 |
| Gene length, protein length | 390 bp, 130 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywpD, ywpB |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 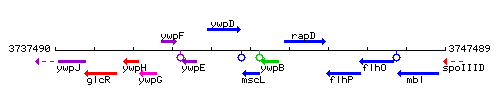
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed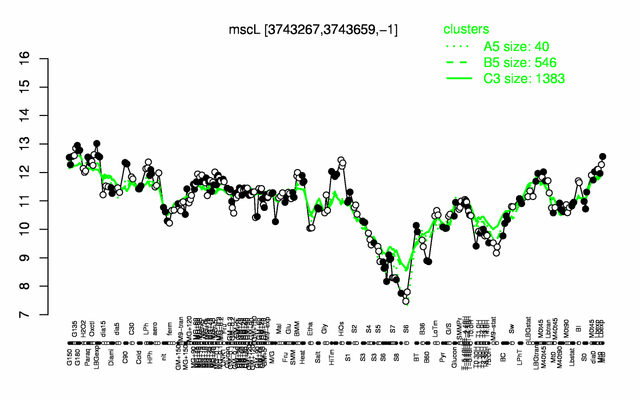
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
coping with hypo-osmotic stress, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU36360
Phenotypes of a mutant
sensitive to osmotic downshock (> 0.5 M) during logarithmic growth PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: mscL family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane PubMed
Database entries
- UniProt: P94585
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: mscL PubMed
- Sigma factor:
- Regulation: expressed in logarithmic phase PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Jan Maarten van Dijl, Groningen, Netherlands
Erhard Bremer, University of Marburg, Germany homepage
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Ian R Booth, Paul Blount
The MscS and MscL families of mechanosensitive channels act as microbial emergency release valves.
J Bacteriol: 2012, 194(18);4802-9
[PubMed:22685280]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ching Kung, Boris Martinac, Sergei Sukharev
Mechanosensitive channels in microbes.
Annu Rev Microbiol: 2010, 64;313-29
[PubMed:20825352]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Valeria Vásquez, Eduardo Perozo
Structural biology: A channel with a twist.
Nature: 2009, 461(7260);47-9
[PubMed:19727188]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Christopher D Pivetti, Ming-Ren Yen, Samantha Miller, Wolfgang Busch, Yi-Hsiung Tseng, Ian R Booth, Milton H Saier
Two families of mechanosensitive channel proteins.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2003, 67(1);66-85, table of contents
[PubMed:12626684]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original Publications