Difference between revisions of "MrpD"
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
<br/><br/><br/><br/> | <br/><br/><br/><br/> | ||
| − | + | <br/><br/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | = [[Categories]] containing this gene/protein = | ||
| Line 120: | Line 116: | ||
* '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=mrpD_3249761_3251242_1 mrpD] {{PubMed|22383849}} | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=mrpD_3249761_3251242_1 mrpD] {{PubMed|22383849}} | ||
| − | * '''Sigma factor:''' | + | * '''[[Sigma factor]]:''' |
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
| Line 147: | Line 143: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | + | <pubmed>11004162,17693497 ,10198001, 19389778 21236240 </pubmed> | |
| − | <pubmed>11004162,17693497 ,10198001, 19389778 </pubmed> | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 10:48, 12 September 2013
- Description: H+ transporter subunit of the Na+/H+ antiporter, multiple resistance and pH homeostasis
| Gene name | mrpD |
| Synonyms | yufD |
| Essential | yes PubMed |
| Product | Na+/H+ antiporter subunit |
| Function | sodium export |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: mrpD | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: MrpD | |
| MW, pI | 53 kDa, 9.488 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1479 bp, 493 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | mrpC, mrpE |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 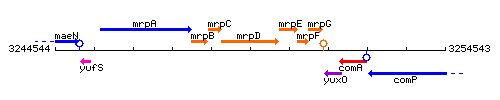
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed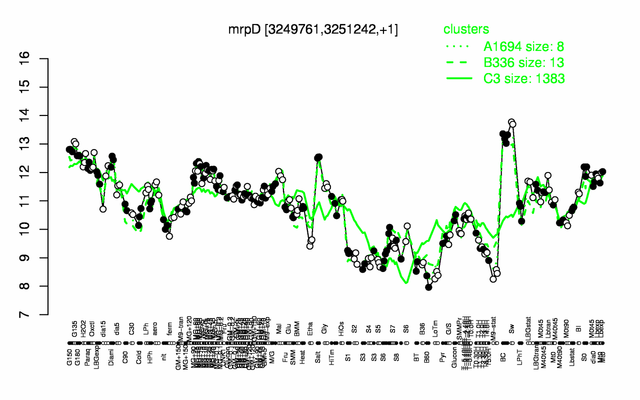
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
transporters/ other, metal ion homeostasis (K, Na, Ca, Mg), essential genes, membrane proteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU31630
Phenotypes of a mutant
essential PubMed
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: H+ transporter subunit of the Na+/H+ antiporter PubMed
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: O05229
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Vamsi K Moparthi, Brijesh Kumar, Cecilie Mathiesen, Cecilia Hägerhäll
Homologous protein subunits from Escherichia coli NADH:quinone oxidoreductase can functionally replace MrpA and MrpD in Bacillus subtilis.
Biochim Biophys Acta: 2011, 1807(4);427-36
[PubMed:21236240]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Yusuke Kajiyama, Masato Otagiri, Junichi Sekiguchi, Toshiaki Kudo, Saori Kosono
The MrpA, MrpB and MrpD subunits of the Mrp antiporter complex in Bacillus subtilis contain membrane-embedded and essential acidic residues.
Microbiology (Reading): 2009, 155(Pt 7);2137-2147
[PubMed:19389778]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Yusuke Kajiyama, Masato Otagiri, Junichi Sekiguchi, Saori Kosono, Toshiaki Kudo
Complex formation by the mrpABCDEFG gene products, which constitute a principal Na+/H+ antiporter in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(20);7511-4
[PubMed:17693497]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Ito, A A Guffanti, W Wang, T A Krulwich
Effects of nonpolar mutations in each of the seven Bacillus subtilis mrp genes suggest complex interactions among the gene products in support of Na(+) and alkali but not cholate resistance.
J Bacteriol: 2000, 182(20);5663-70
[PubMed:11004162]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Ito, A A Guffanti, B Oudega, T A Krulwich
mrp, a multigene, multifunctional locus in Bacillus subtilis with roles in resistance to cholate and to Na+ and in pH homeostasis.
J Bacteriol: 1999, 181(8);2394-402
[PubMed:10198001]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)