Difference between revisions of "HutP"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[yxzL]]'', ''[[hutH]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[yxzL]]'', ''[[hutH]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU39340 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU39340 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU39340 | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU39340 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU39340 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU39340 DNA_with_flanks] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:hutP_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:hutP_context.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 11:40, 14 May 2013
- Description: transcriptional antiterminator of the hut operon
| Gene name | hutP |
| Synonyms | hutP1 |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator |
| Function | regulation of histidine utilization |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: hutP | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: His | |
| MW, pI | 16 kDa, 6.057 |
| Gene length, protein length | 453 bp, 151 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yxzL, hutH |
| Sequences | Protein DNA DNA_with_flanks |
Genetic context 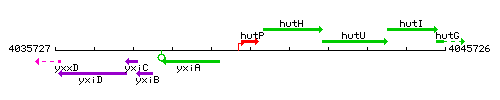
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
| Expression at a glance PubMed 500px | |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of amino acids, transcription factors and their control, RNA binding regulators
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The HutP regulon: hutH-hutU-hutI-hutG-hutM
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU39340
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: hutP family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: P10943
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Robert A Bender
Regulation of the histidine utilization (hut) system in bacteria.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev: 2012, 76(3);565-84
[PubMed:22933560]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Thirumananseri Kumarevel
Structural insights of HutP-mediated regulation of transcription of the hut operon in Bacillus subtilis.
Biophys Chem: 2007, 128(1);1-12
[PubMed:17395359]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Penmetcha K R Kumar, Thirumananseri Kumarevel, Hiroshi Mizuno
Structural basis of HutP-mediated transcription anti-termination.
Curr Opin Struct Biol: 2006, 16(1);18-26
[PubMed:16427271]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Original publications