Difference between revisions of "HemAT"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || movement towards oxygen | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || movement towards oxygen | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http:// | + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Gene expression levels in [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/ ''Subti''Express]''': [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/apps/expression/expression.php?search=BSU10380 hemAT] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/HemAT HemAT] | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/HemAT HemAT] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[yhfU]]'', ''[[yhfW]]'' | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Immediate neighbours''' || ''[[yhfU]]'', ''[[yhfW]]'' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"|'''Sequences'''||[http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence-aa?type=GENE&object=BSU10380 Protein] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/sequence?type=GENE&object=BSU10380 DNA] [http://bsubcyc.org/BSUB/seq-selector?chromosome=CHROM-1&object=BSU10380 Advanced_DNA] |
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:hemAT_context.gif]] | |colspan="2" | '''Genetic context''' <br/> [[Image:hemAT_context.gif]] | ||
Revision as of 12:29, 13 May 2013
- Description: soluble chemotaxis receptor, heme-containing O(2) sensor protein
| Gene name | hemAT |
| Synonyms | yhfV |
| Essential | no |
| Product | haem-based aerotactic transducer |
| Function | movement towards oxygen |
| Gene expression levels in SubtiExpress: hemAT | |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: HemAT | |
| MW, pI | 48 kDa, 5.441 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1296 bp, 432 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | yhfU, yhfW |
| Sequences | Protein DNA Advanced_DNA |
Genetic context 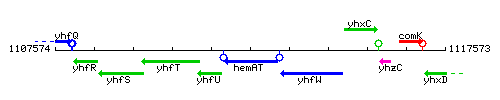
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Expression at a glance PubMed
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU10380
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family:
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s): heme
- Effectors of protein activity:
Database entries
- UniProt: O07621
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon: hemAT PubMed
- Regulation:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
- in minimal medium, HemAT is present with 19,000 +/- 3,900 molecules per cell PubMed
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Additional publications: PubMed
Carmine G Monteferrante, Calum MacKichan, Elodie Marchadier, Maria-Victoria Prejean, Rut Carballido-López, Jan Maarten van Dijl
Mapping the twin-arginine protein translocation network of Bacillus subtilis.
Proteomics: 2013, 13(5);800-11
[PubMed:23180473]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Vincent J Cannistraro, George D Glekas, Christopher V Rao, George W Ordal
Cellular stoichiometry of the chemotaxis proteins in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 2011, 193(13);3220-7
[PubMed:21515776]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Hideaki Yoshimura, Shiro Yoshioka, Katsuaki Kobayashi, Takehiro Ohta, Takeshi Uchida, Minoru Kubo, Teizo Kitagawa, Shigetoshi Aono
Specific hydrogen-bonding networks responsible for selective O2 sensing of the oxygen sensor protein HemAT from Bacillus subtilis.
Biochemistry: 2006, 45(27);8301-7
[PubMed:16819829]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Masakuni Serizawa, Hiroki Yamamoto, Hirotake Yamaguchi, Yasutaro Fujita, Kazuo Kobayashi, Naotake Ogasawara, Junichi Sekiguchi
Systematic analysis of SigD-regulated genes in Bacillus subtilis by DNA microarray and Northern blotting analyses.
Gene: 2004, 329;125-36
[PubMed:15033535]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Hou, T Freitas, R W Larsen, M Piatibratov, V Sivozhelezov, A Yamamoto, E A Meleshkevitch, M Zimmer, G W Ordal, M Alam
Globin-coupled sensors: a class of heme-containing sensors in Archaea and Bacteria.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 2001, 98(16);9353-8
[PubMed:11481493]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Hou, R W Larsen, D Boudko, C W Riley, E Karatan, M Zimmer, G W Ordal, M Alam
Myoglobin-like aerotaxis transducers in Archaea and Bacteria.
Nature: 2000, 403(6769);540-4
[PubMed:10676961]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)