Difference between revisions of "AckA"
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
* '''Operon:''' ''[[ackA]]'' {{PubMed|8226682}} | * '''Operon:''' ''[[ackA]]'' {{PubMed|8226682}} | ||
| − | * '''[ | + | * '''Expression browser:''' [http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/cgi-bin/seb/viewdetail.py?id=ackA_3015111_3016298_-1 ackA] {{PubMed|22383849}} |
| + | |||
| + | * '''Sigma factor:''' [[SigA]] {{PubMed|8226682}} | ||
* '''Regulation:''' | * '''Regulation:''' | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 16 April 2012
- Description: acetate kinase
| Gene name | ackA |
| Synonyms | |
| Essential | no |
| Product | acetate kinase |
| Function | overflow metabolism |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Central C-metabolism | |
| MW, pI | 42 kDa, 5.191 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1185 bp, 395 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | moaB, ytxK |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 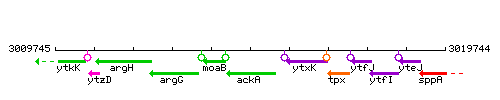
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
ATP synthesis, carbon core metabolism
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU29470
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: ATP + acetate = ADP + acetyl phosphate (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: acetokinase family (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Paralogous protein(s):
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization: cytoplasm (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure: 2IIR (from Thermotoga maritima, 54% identity, 73% similarity)
- UniProt: P37877
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 2.7.2.1
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Linc Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA Homepage
Your additional remarks
References