Difference between revisions of "SacT"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of sucrose utilization | |style="background:#ABCDEF;" align="center"|'''Function''' || regulation of sucrose utilization | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Interactions involving this protein in [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/startpage/start/ ''Subt''Interact]''': [http://cellpublisher.gobics.de/subtinteract/interactionList/2/SacT SacT] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbohydrate_metabolic_pathways.html Sugar catabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/stress_response.html Stress]''' | |colspan="2" style="background:#FAF8CC;" align="center"| '''Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in [[SubtiPathways|''Subti''Pathways]]: <br/>[http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/carbohydrate_metabolic_pathways.html Sugar catabolism], [http://subtiwiki.uni-goettingen.de/pathways/stress_response.html Stress]''' | ||
Revision as of 12:25, 28 July 2011
- Description: transcriptional antiterminator for the sacP-sacA-ywdA operon
| Gene name | sacT |
| Synonyms | ipa-47d |
| Essential | no |
| Product | transcriptional antiterminator |
| Function | regulation of sucrose utilization |
| Interactions involving this protein in SubtInteract: SacT | |
| Metabolic function and regulation of this protein in SubtiPathways: Sugar catabolism, Stress | |
| MW, pI | 31 kDa, 5.587 |
| Gene length, protein length | 828 bp, 276 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | ywcJ, ywcI |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 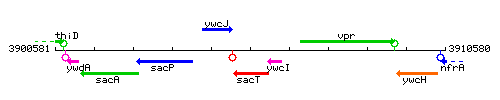
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
Categories containing this gene/protein
utilization of specific carbon sources, transcription factors and their control, RNA binding regulators, phosphoproteins
This gene is a member of the following regulons
The SacT regulon: sacP-sacA-ywdA
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU38070
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: binding to the mRNA of the sacP-sacA operon, causes transcription antitermination (in presence of sucrose and absence of glucose)
- Protein family: transcriptional antiterminator bglG family (according to Swiss-Prot) BglG family of antiterminators
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Localization:
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P26212
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Regulation:
- repressed by casamino acids PubMed
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant: GP429 (spc), available in Stülke lab
- Expression vector:
- for expression, purification of both PRDs in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP166, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-1 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP426, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-2 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag, in pWH844: pGP427, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-1 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pGP570: pGP439, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of PRD-2 in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pGP570: pGP440, available in Stülke lab
- for expression, purification of the RNA-binding domain in E. coli with N-terminal His-tag and thrombin cleavage site, in pGP570: pGP571, available in Stülke lab
- for expression of the RNA-binding domain in B. subtilis, in pBQ200: pGP446, available in Stülke lab
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Sebastian Hübner, Nathalie Declerck, Christine Diethmaier, Dominique Le Coq, Stephane Aymerich, Jörg Stülke
Prevention of cross-talk in conserved regulatory systems: identification of specificity determinants in RNA-binding anti-termination proteins of the BglG family.
Nucleic Acids Res: 2011, 39(10);4360-72
[PubMed:21278164]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(I p)
Ulrike Mäder, Georg Homuth, Christian Scharf, Knut Büttner, Rüdiger Bode, Michael Hecker
Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis gene expression modulated by amino acid availability.
J Bacteriol: 2002, 184(15);4288-95
[PubMed:12107147]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Arnaud, M Débarbouillé, G Rapoport, M H Saier, J Reizer
In vitro reconstitution of transcriptional antitermination by the SacT and SacY proteins of Bacillus subtilis.
J Biol Chem: 1996, 271(31);18966-72
[PubMed:8702561]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
S Aymerich, M Steinmetz
Specificity determinants and structural features in the RNA target of the bacterial antiterminator proteins of the BglG/SacY family.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A: 1992, 89(21);10410-4
[PubMed:1279678]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Arnaud, P Vary, M Zagorec, A Klier, M Debarbouille, P Postma, G Rapoport
Regulation of the sacPA operon of Bacillus subtilis: identification of phosphotransferase system components involved in SacT activity.
J Bacteriol: 1992, 174(10);3161-70
[PubMed:1577686]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
M Debarbouille, M Arnaud, A Fouet, A Klier, G Rapoport
The sacT gene regulating the sacPA operon in Bacillus subtilis shares strong homology with transcriptional antiterminators.
J Bacteriol: 1990, 172(7);3966-73
[PubMed:2163394]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)