Difference between revisions of "FliY"
(→Basic information/ Evolution) |
|||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
** [[Spo0A]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|14651647}} | ** [[Spo0A]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|14651647}} | ||
** [[CodY]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|12730172}} | ** [[CodY]]: transcription repression {{PubMed|12730172}} | ||
| + | ** [[DegU]] (non-phosphorylated): transcription activation {{PubMed|17850253}} | ||
* '''Additional information:''' | * '''Additional information:''' | ||
| Line 124: | Line 125: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
| − | <pubmed>14749334,1447979,,14651647, 9657996,8157612,15175317,12920116</pubmed> | + | <pubmed>14749334,1447979,,14651647, 9657996,8157612,15175317,12920116 17850253</pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 31 July 2010
- Description: flagellar motor switch protein
| Gene name | fliY |
| Synonyms | cheD |
| Essential | no |
| Product | flagellar motor switch protein |
| Function | movement and chemotaxis |
| MW, pI | 40 kDa, 4.117 |
| Gene length, protein length | 1134 bp, 378 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | fliM, cheY |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 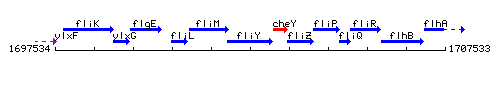
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU16320
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity:
- Protein family: fliN/mopA/spaO family (according to Swiss-Prot) cheC family
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization: cell membrane (according to Swiss-Prot)
Database entries
- Structure:
- UniProt: P24073
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number:
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Operon:
- Regulatory mechanism:
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Kazuo Kobayashi
Gradual activation of the response regulator DegU controls serial expression of genes for flagellum formation and biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2007, 66(2);395-409
[PubMed:17850253]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
H Werhane, P Lopez, M Mendel, M Zimmer, G W Ordal, L M Márquez-Magaña
The last gene of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis, ylxL, is required for maximal sigmaD function.
J Bacteriol: 2004, 186(12);4025-9
[PubMed:15175317]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hendrik Szurmant, Travis J Muff, George W Ordal
Bacillus subtilis CheC and FliY are members of a novel class of CheY-P-hydrolyzing proteins in the chemotactic signal transduction cascade.
J Biol Chem: 2004, 279(21);21787-92
[PubMed:14749334]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Virginie Molle, Masaya Fujita, Shane T Jensen, Patrick Eichenberger, José E González-Pastor, Jun S Liu, Richard Losick
The Spo0A regulon of Bacillus subtilis.
Mol Microbiol: 2003, 50(5);1683-701
[PubMed:14651647]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Hendrik Szurmant, Michael W Bunn, Vincent J Cannistraro, George W Ordal
Bacillus subtilis hydrolyzes CheY-P at the location of its action, the flagellar switch.
J Biol Chem: 2003, 278(49);48611-6
[PubMed:12920116]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
W Estacio, S S Anna-Arriola, M Adedipe, L M Márquez-Magaña
Dual promoters are responsible for transcription initiation of the fla/che operon in Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1998, 180(14);3548-55
[PubMed:9657996]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
L M Márquez-Magaña, M J Chamberlin
Characterization of the sigD transcription unit of Bacillus subtilis.
J Bacteriol: 1994, 176(8);2427-34
[PubMed:8157612]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
D S Bischoff, G W Ordal
Identification and characterization of FliY, a novel component of the Bacillus subtilis flagellar switch complex.
Mol Microbiol: 1992, 6(18);2715-23
[PubMed:1447979]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)