Difference between revisions of "FabI"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
=== Database entries === | === Database entries === | ||
| − | * '''Structure:''' | + | * '''Structure:''' [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=1DFI 1DFI] (the enzyme from ''E. coli'' in complex with NAD) {{PubMed|8953047}} |
* '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P54616 P54616] | * '''UniProt:''' [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P54616 P54616] | ||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
<pubmed> 15952903 17919287</pubmed> | <pubmed> 15952903 17919287</pubmed> | ||
==Original Publications== | ==Original Publications== | ||
| − | <pubmed>12737802,17114254, </pubmed> | + | <pubmed>12737802,17114254, 8953047 </pubmed> |
[[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | [[Category:Protein-coding genes]] | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 6 January 2010
- Description: enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase
| Gene name | fabI |
| Synonyms | yjbW |
| Essential | no |
| Product | enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase |
| Function | fatty acid biosynthesis |
| MW, pI | 27 kDa, 5.605 |
| Gene length, protein length | 774 bp, 258 aa |
| Immediate neighbours | thiD, cotO |
| Get the DNA and protein sequences (Barbe et al., 2009) | |
Genetic context 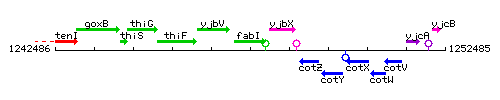
This image was kindly provided by SubtiList
| |
Contents
The gene
Basic information
- Locus tag: BSU11720
Phenotypes of a mutant
Database entries
- DBTBS entry: [1]
- SubtiList entry: [2]
Additional information
The protein
Basic information/ Evolution
- Catalyzed reaction/ biological activity: Acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NAD+ = trans-2,3-dehydroacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] + NADH (according to Swiss-Prot)
- Protein family: FabI subfamily (according to Swiss-Prot)
Extended information on the protein
- Kinetic information:
- Domains:
- Modification:
- Cofactor(s):
- Effectors of protein activity:
- Interactions:
- Localization:
Database entries
- UniProt: P54616
- KEGG entry: [3]
- E.C. number: 1.3.1.9
Additional information
Expression and regulation
- Additional information:
Biological materials
- Mutant:
- Expression vector:
- lacZ fusion:
- GFP fusion:
- two-hybrid system:
- Antibody:
Labs working on this gene/protein
Your additional remarks
References
Reviews
Original Publications
Helena B Thomaides, Ella J Davison, Lisa Burston, Hazel Johnson, David R Brown, Alison C Hunt, Jeffery Errington, Lloyd Czaplewski
Essential bacterial functions encoded by gene pairs.
J Bacteriol: 2007, 189(2);591-602
[PubMed:17114254]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
Gustavo E Schujman, Luciana Paoletti, Alan D Grossman, Diego de Mendoza
FapR, a bacterial transcription factor involved in global regulation of membrane lipid biosynthesis.
Dev Cell: 2003, 4(5);663-72
[PubMed:12737802]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)
C Baldock, J B Rafferty, S E Sedelnikova, P J Baker, A R Stuitje, A R Slabas, T R Hawkes, D W Rice
A mechanism of drug action revealed by structural studies of enoyl reductase.
Science: 1996, 274(5295);2107-10
[PubMed:8953047]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)